A myopathy-linked tropomyosin mutation severely alters thin filament conformational changes during activation
- PMID: 20457903
- PMCID: PMC2906900
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1001733107
A myopathy-linked tropomyosin mutation severely alters thin filament conformational changes during activation
Abstract
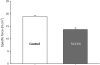
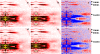
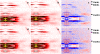
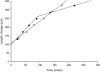
Human point mutations in beta- and gamma-tropomyosin induce contractile deregulation, skeletal muscle weakness, and congenital myopathies. The aim of the present study was to elucidate the hitherto unknown underlying molecular mechanisms. Hence, we recorded and analyzed the X-ray diffraction patterns of human membrane-permeabilized muscle cells expressing a particular beta-tropomyosin mutation (R133W) associated with a loss in cell force production, in vivo muscle weakness, and distal arthrogryposis. Upon addition of calcium, we notably observed less intensified changes, compared with controls, (i) in the second (1/19 nm(-1)), sixth (1/5.9 nm(-1)), and seventh (1/5.1 nm(-1)) actin layer lines of cells set at a sarcomere length, allowing an optimal thin-thick filament overlap; and (ii) in the second actin layer line of overstretched cells. Collectively, these results directly prove that during activation, switching of a positive to a neutral charge at position 133 in the protein partially hinders both calcium- and myosin-induced tropomyosin movement over the thin filament, blocking actin conformational changes and consequently decreasing the number of cross-bridges and subsequent force production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Perry SV. Vertebrate tropomyosin: Distribution, properties and function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2001;22:5–49. - PubMed
-
- Lees-Miller JP, Helfman DM. The molecular basis for tropomyosin isoform diversity. Bioessays. 1991;13:429–437. - PubMed
-
- Ochala J. Thin filament proteins mutations associated with skeletal myopathies: Defective regulation of muscle contraction. J Mol Med. 2008;86:1197–1204. - PubMed
-
- Tajsharghi H, Kimber E, Holmgren D, Tulinius M, Oldfors A. Distal arthrogryposis and muscle weakness associated with a beta-tropomyosin mutation. Neurology. 2007;68:772–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

