Acute stress modulates genotype effects on amygdala processing in humans
- PMID: 20457919
- PMCID: PMC2906860
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003514107
Acute stress modulates genotype effects on amygdala processing in humans
Abstract
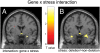
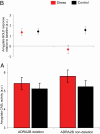
Probing gene-environment interactions that affect neural processing is crucial for understanding individual differences in behavior and disease vulnerability. Here, we tested whether the current environmental context, which affects the acute brain state, modulates genotype effects on brain function in humans. We manipulated the context by inducing acute psychological stress, which increases noradrenergic activity, and probed its effect on tonic activity and phasic responses in the amygdala using two MRI techniques: conventional blood oxygen level-dependent functional MRI and arterial spin labeling. We showed that only carriers of a common functional deletion in ADRA2B, the gene coding for the alpha2b-adrenoreceptor, displayed increased phasic amygdala responses under stress. Tonic activity, reflecting the perfusion of the amygdala, increased independently of genotype after stress induction. Thus, when tonic activity was heightened by stress, only deletion carriers showed increased amygdala responses. Our results demonstrate that genetic effects on brain operations can be state dependent, such that they only become apparent under specific, often environmentally controlled, conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Green AE, et al. Using genetic data in cognitive neuroscience: From growing pains to genuine insights. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:710–720. - PubMed
-
- Hariri AR, et al. Serotonin transporter genetic variation and the response of the human amygdala. Science. 2002;297:400–403. - PubMed
-
- Caspi A, Moffitt TE. Gene-environment interactions in psychiatry: Joining forces with neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:583–590. - PubMed
-
- Caspi A, et al. Influence of life stress on depression: Moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science. 2003;301:386–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

