An inherited variable poly-T repeat genotype in TOMM40 in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 20457951
- PMCID: PMC3140162
- DOI: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.88
An inherited variable poly-T repeat genotype in TOMM40 in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
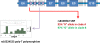
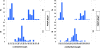
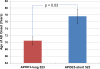
I coauthored a recently published research article describing a variable length, poly-T polymorphism in the TOMM40 gene, adjacent to apolipoprotein E (APOE) on chromosome 19, that accounts for the age at onset distribution for a complex disease, late-onset Alzheimer disease. These new data explain the mean age at disease onset for patients with the APOE4/4 genotype and differentiate 2 forms of TOMM40 poly-T polymorphisms linked to APOE, with each form associated with a different age at disease onset distribution. When linked to APOE3 (encoding the epsilon3 isoform of APOE), the longer TOMM40 poly-T repeats (19-39 nucleotides) at the rs10524523 (hereafter, 523) locus are associated with earlier age at onset and the shorter TOMM40 523 alleles (11-16 nucleotides) are associated with later age at onset. The data suggest that the poly-T alleles are codominant, with the age at onset phenotype determined by the 2 inherited 523 alleles, but with variable expressivity. Additional data will further refine the relationship between the length of the poly-T alleles and age at disease onset and determine if the relationship is linear.
Figures

References
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261(5123):921–923. - PubMed
-
- Eastman P. Safe ways to speed CNS drugs to patients, including provisional approval. Neurology Today. American Academy of Neurology. 2008;8(7):6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

