Anthropometric measures, body mass index, and pancreatic cancer: a pooled analysis from the Pancreatic Cancer Cohort Consortium (PanScan)
- PMID: 20458087
- PMCID: PMC2920035
- DOI: 10.1001/archinternmed.2010.63
Anthropometric measures, body mass index, and pancreatic cancer: a pooled analysis from the Pancreatic Cancer Cohort Consortium (PanScan)
Abstract
Background: Obesity has been proposed as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer.
Methods: Pooled data were analyzed from the National Cancer Institute Pancreatic Cancer Cohort Consortium (PanScan) to study the association between prediagnostic anthropometric measures and risk of pancreatic cancer. PanScan applied a nested case-control study design and included 2170 cases and 2209 control subjects. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using unconditional logistic regression for cohort-specific quartiles of body mass index (BMI [calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared]), weight, height, waist circumference, and waist to hip ratio as well as conventional BMI categories (underweight, <18.5; normal weight, 18.5-24.9; overweight, 25.0-29.9; obese, 30.0-34.9; and severely obese, > or = 35.0). Models were adjusted for potential confounders.
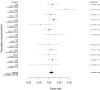
Results: In all of the participants, a positive association between increasing BMI and risk of pancreatic cancer was observed (adjusted OR for the highest vs lowest BMI quartile, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.12-1.58; P(trend) < .001). In men, the adjusted OR for pancreatic cancer for the highest vs lowest quartile of BMI was 1.33 (95% CI, 1.04-1.69; P(trend) < .03), and in women it was 1.34 (95% CI, 1.05-1.70; P(trend) = .01). Increased waist to hip ratio was associated with increased risk of pancreatic cancer in women (adjusted OR for the highest vs lowest quartile, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.31-2.69; P(trend) = .003) but less so in men.
Conclusions: These findings provide strong support for a positive association between BMI and pancreatic cancer risk. In addition, centralized fat distribution may increase pancreatic cancer risk, especially in women.
Figures


References
-
- American Cancer Society . Cancer Facts & Figures - 2009. American Cancer Society, Inc.; Atlanta: 2009.
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74–108. - PubMed
-
- Edwards BK, Brown ML, Wingo PA, et al. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2002, featuring population-based trends in cancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(19):1407–1427. - PubMed
-
- Gapstur SM, Gann P. Is pancreatic cancer a preventable disease? JAMA. 2001;286(8):967–968. - PubMed
-
- Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2004;363(9414):1049–1057. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01-CN-75022/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA098661/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN075022/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA105069/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032108/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025515/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA050385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA73790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25524/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25513/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-RC-45035/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25511/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025512/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082729/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25514/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032105/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025404/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH042107/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025516/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- N01WH22110,/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25512/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025511/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01AG018033/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025511/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025522/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025522/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025513/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH022110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032100/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010195/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032111/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- N01 WH032122/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032118/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025524/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025476/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025514/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U105630924/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01-CN-25515/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES000260/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA034588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025518/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA138313/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN075022/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA124908/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA102701/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025512/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025524/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA034588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA098661/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032115/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025513/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25404/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025476/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA70867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25516/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA140790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025515/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA82729/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 RC037004/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01-CN-25476/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA040360/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA105069/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN045165/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097193/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH032119/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH042129/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH024152/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- ES000260/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25518/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025514/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG018033/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-CN-25522/CN/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

