Kidney injury molecule-1 outperforms traditional biomarkers of kidney injury in preclinical biomarker qualification studies
- PMID: 20458318
- PMCID: PMC2885849
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.1623
Kidney injury molecule-1 outperforms traditional biomarkers of kidney injury in preclinical biomarker qualification studies
Abstract
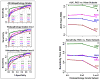
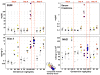
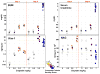
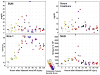
Kidney toxicity accounts both for the failure of many drug candidates as well as considerable patient morbidity. Whereas histopathology remains the gold standard for nephrotoxicity in animal systems, serum creatinine (SCr) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) are the primary options for monitoring kidney dysfunction in humans. The transmembrane tubular protein kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1) was previously reported to be markedly induced in response to renal injury. Owing to the poor sensitivity and specificity of SCr and BUN, we used rat toxicology studies to compare the diagnostic performance of urinary Kim-1 to BUN, SCr and urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) as predictors of kidney tubular damage scored by histopathology. Kim-1 outperforms SCr, BUN and urinary NAG in multiple rat models of kidney injury. Urinary Kim-1 measurements may facilitate sensitive, specific and accurate prediction of human nephrotoxicity in preclinical drug screens. This should enable early identification and elimination of compounds that are potentially nephrotoxic.
Figures


Comment in
-
A roadmap for biomarker qualification.Nat Biotechnol. 2010 May;28(5):444-5. doi: 10.1038/nbt0510-444. Nat Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20458313 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3365–3370. - PubMed
-
- Choudhury D, Ziauddin A. Drug-associated renal dysfunction and injury. Nature Clinical Practice Nephrology. 2005;2:80–91. - PubMed
-
- Ichimura T, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4135–4142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

