Developing a quantitative measurement system for assessing heterotopic ossification and monitoring the bioelectric metrics from electrically induced osseointegration in the residual limb of service members
- PMID: 20458630
- PMCID: PMC3166247
- DOI: 10.1007/s10439-010-0050-2
Developing a quantitative measurement system for assessing heterotopic ossification and monitoring the bioelectric metrics from electrically induced osseointegration in the residual limb of service members
Abstract
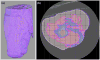
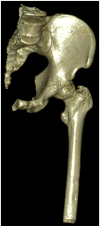
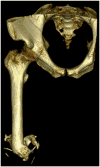
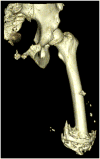
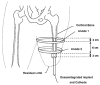
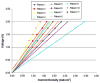
Poor prosthetic fit is often the result of heterotopic ossification (HO), a frequent problem following blast injuries for returning service members. Osseointegration technology offers an advantage for individuals with significant HO and poor socket tolerance by using direct skeletal attachment of a prosthesis to the distal residual limb, but remains limited due to prolonged post-operative rehabilitation regimens. Therefore, electrical stimulation has been proposed as a catalyst for expediting skeletal attachment and the bioelectric effects of HO were evaluated using finite element analysis in 11 servicemen with transfemoral amputations. Retrospective computed tomography (CT) scans provided accurate reconstructions, and volume conductor models demonstrated the variability in residual limb anatomy and necessity for patient-specific modeling to characterize electrical field variance if patients were to undergo a theoretical osseointegration of a prosthesis. In this investigation, the volume of HO was statistically significant when selecting the optimal potential difference for enhanced skeletal fixation, since higher HO volumes required increased voltages at the periprosthetic bone (p = 0.024, r = 0.670). Results from Spearman's rho correlations also indicated that the age of the subject and volume of HO were statistically significant and inversely proportional, in which younger service members had a higher frequency of HO (p = 0.041, r = -0.622). This study demonstrates that the volume of HO and age may affect the voltage threshold necessary to improve current osseointegration procedures.
Figures



References
-
- Ahrengart L. Periarticular heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. Risk factors and consequences. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;263:49–58. - PubMed
-
- Akai M, Hayashi K. Effect of electrical stimulation on musculoskeletal systems; a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials. Bioelectromagnetics. 2002;23:132–143. - PubMed
-
- Albrektsson T, Albrektsson B. Osseointegration of bone implants. A review of an alternative mode of fixation. Acta Orthop Scand. 1987;58:567–577. - PubMed
-
- Andersen R, Davis S, Scoville C. Rehabilitation of military amputees: from injury to independence. Orthopedics. 2008;31:1000–1002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

