Static and dynamic light scattering of healthy and malaria-parasite invaded red blood cells
- PMID: 20459219
- PMCID: PMC2862053
- DOI: 10.1117/1.3369966
Static and dynamic light scattering of healthy and malaria-parasite invaded red blood cells
Abstract
We present the light scattering of individual Plasmodium falciparum-parasitized human red blood cells (Pf-RBCs), and demonstrate progressive alterations to the scattering signal arising from the development of malaria-inducing parasites. By selectively imaging the electric fields using quantitative phase microscopy and a Fourier transform light scattering technique, we calculate the light scattering maps of individual Pf-RBCs. We show that the onset and progression of pathological states of the Pf-RBCs can be clearly identified by the static scattering maps. Progressive changes to the biophysical properties of the Pf-RBC membrane are captured from dynamic light scattering.
Figures
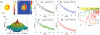

References
-
- Berne B. and Pecora R., Dynamic Light Scattering: with Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics, Dover Publications, Mineola, New York: (2000).
-
- Subramanian H., Pradhan P., Liu Y., Capoglu I., Li X., Rogers J., Heifetz A., Kunte D., Roy H., Taflove A., and Backman V., “Optical methodology for detecting histologically unapparent nanoscale consequences of genetic alterations in biological cells,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. PNASA6 105(51), 20118 (2008).10.1073/pnas.0804723105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

