Adhesion of renal carcinoma cells to endothelial cells depends on PKCmu
- PMID: 20459627
- PMCID: PMC2873397
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-183
Adhesion of renal carcinoma cells to endothelial cells depends on PKCmu
Abstract
Background: The formation of metastases includes the separation of tumor cells from the primary tumor, cell migration into subendothelial tissue and cell proliferation in secondary organ. In this process, cell adhesion of tumor cells to the endothelium is an essential requirement for formation of metastases. Protein kinase C (PKC) regulates adhesion and proliferation. To identify a relation between PKC isoforms and tumor progression in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), the influence of PKC isoforms on cell adhesion and proliferation, and possible influences of integrins were analyzed in RCC cells.
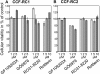
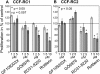
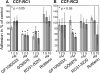
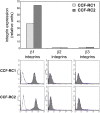
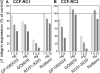
Methods: The experiments were performed in the RCC cell lines CCF-RC1 and CCF-RC2 after pre-incubation (16 h) with the PKC inhibitors GF109203X (inhibits PKCalpha, betaI, betaII, gamma, delta and epsilon), GO6976 (inhibits PKCalpha, betaI and mu), RO31-8220 (inhibits PKCalpha, betaI, betaII, gamma and epsilon) and rottlerin (inhibits PKCdelta). Cell adhesion was assessed through adherence of RCC cells to an endothelial monolayer. Cell proliferation was analyzed by a BrdU incorporation assay. The expression of beta1 integrins was analyzed by flow cytometry.
Results: In CCF-RC1 cells, cell adhesion was significantly reduced by GO6976 to 55% and by RO31-8220 to 45% of control. In CCF-RC2 cells, only GO6976 induced a significant reduction of cell adhesion to 50% of control levels. Proliferation of both cell lines was reduced by rottlerin to 39% and 45% of control, respectively. The beta1 integrin expression on the cell surface of CCF-RC1 and CCR-RC2 cells was decreased by RO31-8220 to 8% and 7% of control, respectively. beta2 and beta3 integrins were undetectable in both cell lines.
Conclusions: The combination of the PKC inhibitors leads to the assumption that PKCmu influences cell adhesion in CCF-RC1 and CCF-RC2 cells, whereas in CCF-RC1 cells PKCepsilon also seems to be involved in this process. The expression of beta1 integrins appears to be regulated in particular by PKCepsilon. Cell proliferation was inhibited by rottlerin, so that PKCdelta might be involved in cell proliferation in these cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of beta1 integrin expression by PKCepsilon in renal cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2004 Oct;25(4):1157-63. Int J Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15375568
-
Migration of renal carcinoma cells is dependent on protein kinase Cdelta via beta1 integrin and focal adhesion kinase.Int J Oncol. 2008 May;32(5):1125-31. Int J Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18425341
-
Characterization of two cell lines with distinct phenotypes and genotypes established from a patient with renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 15;49(24 Pt 1):7064-71. Cancer Res. 1989. PMID: 2582448
-
Protein kinase C in human renal cell carcinomas: role in invasion and differential isoenzyme expression.Br J Cancer. 2000 Mar;82(5):1063-9. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.1999.1043. Br J Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10737390 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus alters adhesion and migration behavior of renal cell carcinoma cells through an integrin α5- and integrin β3-dependent mechanism.Neoplasia. 2014 Apr;16(4):291-300. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.03.011. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 24862756 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lysophosphatidic acid enhances breast cancer cells-mediated osteoclastogenesis.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;22(5):503-511. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.5.503. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30181697 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) promotes development of bone metastasis in renal cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2018 Mar 2;9(21):15766-15779. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24607. eCollection 2018 Mar 20. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29644008 Free PMC article.
-
Co-administration of tyrosine kinase inhibitors with rottlerin in metastatic prostate cancer cells.EXCLI J. 2021 Nov 19;20:1585-1596. doi: 10.17179/excli2021-3980. eCollection 2021. EXCLI J. 2021. PMID: 34924906 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase D signaling in cancer: A friend or foe?Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017 Aug;1868(1):283-294. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.05.008. Epub 2017 May 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28577984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of protein kinase D1 in cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Aug;9(8):985-96. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0365. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21680539 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zernecke A, Weber KS, Erwig LP, Kluth DC, Schröppel B, Rees AJ, Weber C. Combinatorial model of chemokine involvement in glomerular monocyte recruitment: role of CXC chemokine receptor 2 in infiltration during nephrotoxic nephritis. J Immunol. 2001;166:5755–5762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

