The serendipitous origin of chordate secretin peptide family members
- PMID: 20459630
- PMCID: PMC2880984
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-135
The serendipitous origin of chordate secretin peptide family members
Abstract
Background: The secretin family is a pleotropic group of brain-gut peptides with affinity for class 2 G-protein coupled receptors (secretin family GPCRs) proposed to have emerged early in the metazoan radiation via gene or genome duplications. In human, 10 members exist and sequence and functional homologues and ligand-receptor pairs have been characterised in representatives of most vertebrate classes. Secretin-like family GPCR homologues have also been isolated in non-vertebrate genomes however their corresponding ligands have not been convincingly identified and their evolution remains enigmatic.
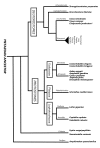
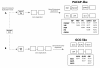
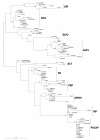
Results: In silico sequence comparisons failed to retrieve a non-vertebrate (porifera, cnidaria, protostome and early deuterostome) secretin family homologue. In contrast, secretin family members were identified in lamprey, several teleosts and tetrapods and comparative studies revealed that sequence and structure is in general maintained. Sequence comparisons and phylogenetic analysis revealed that PACAP, VIP and GCG are the most highly conserved members and two major peptide subfamilies exist; i) PACAP-like which includes PACAP, PRP, VIP, PH, GHRH, SCT and ii) GCG-like which includes GCG, GLP1, GLP2 and GIP. Conserved regions flanking secretin family members were established by comparative analysis of the Takifugu, Xenopus, chicken and human genomes and gene homologues were identified in nematode, Drosophila and Ciona genomes but no gene linkage occurred. However, in Drosophila and nematode genes which flank vertebrate secretin family members were identified in the same chromosome.
Conclusions: Receptors of the secretin-like family GPCRs are present in protostomes but no sequence homologues of the vertebrate cognate ligands have been identified. It has not been possible to determine when the ligands evolved but it seems likely that it was after the protostome-deuterostome divergence from an exon that was part of an existing gene or gene fragment by rounds of gene/genome duplication. The duplicate exon under different evolutionary pressures originated the chordate PACAP-like and GCG-like subfamily groups. This event occurred after the emergence of the metazoan secretin GPCRs and led to the establishment of novel peptide-receptor interactions that contributed to the generation of novel physiological functions in the chordate lineage.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evolution of secretin family GPCR members in the metazoa.BMC Evol Biol. 2006 Dec 13;6:108. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-6-108. BMC Evol Biol. 2006. PMID: 17166275 Free PMC article.
-
Fish genomes provide novel insights into the evolution of vertebrate secretin receptors and their ligand.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014 Dec 1;209:82-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.05.025. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24906176
-
Nematode and arthropod genomes provide new insights into the evolution of class 2 B1 GPCRs.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 20;9(3):e92220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092220. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24651821 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular evolution of GPCRs: Secretin/secretin receptors.J Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Jun;52(3):T1-14. doi: 10.1530/JME-13-0259. J Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24868104 Review.
-
Passage of VIP/PACAP/secretin family across the blood-brain barrier: therapeutic effects.Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10(12):1325-40. doi: 10.2174/1381612043384934. Curr Pharm Des. 2004. PMID: 15134484 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic and intestinal endocrine cells in zebrafish share common transcriptomic signatures and regulatory programmes.BMC Biol. 2020 Aug 31;18(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00840-1. BMC Biol. 2020. PMID: 32867764 Free PMC article.
-
Tracing the Origins of the Pituitary Adenylate-Cyclase Activating Polypeptide (PACAP).Front Neurosci. 2020 May 20;14:366. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00366. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32508559 Free PMC article.
-
PACAP and migraine headache: immunomodulation of neural circuits in autonomic ganglia and brain parenchyma.J Headache Pain. 2018 Mar 13;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s10194-018-0850-6. J Headache Pain. 2018. PMID: 29536279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does Kisspeptin Belong to the Proposed RF-Amide Peptide Family?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Aug 13;5:134. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00134. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 25165463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PACAP/GCGa Is an Important Modulator of the Amphioxus CNS-Hatschek's Pit Axis, the Homolog of the Vertebrate Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis in the Basal Chordates.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 14;13:850040. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.850040. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35498398 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jorpes JE, Mutt V. The gastrointestinal hormones, secretin and cholecystokinin-pancreozymin. Ann Intern Med. 1961;55:395–405. - PubMed
-
- Vaudry D, Gonzalez BJ, Basille M, Yon L, Fournier A, Vaudry H. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide and its receptors: from structure to functions. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:269–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

