Predicting environmental chemical factors associated with disease-related gene expression data
- PMID: 20459635
- PMCID: PMC2880288
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-8794-3-17
Predicting environmental chemical factors associated with disease-related gene expression data
Abstract
Background: Many common diseases arise from an interaction between environmental and genetic factors. Our knowledge regarding environment and gene interactions is growing, but frameworks to build an association between gene-environment interactions and disease using preexisting, publicly available data has been lacking. Integrating freely-available environment-gene interaction and disease phenotype data would allow hypothesis generation for potential environmental associations to disease.
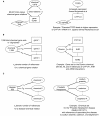
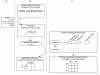
Methods: We integrated publicly available disease-specific gene expression microarray data and curated chemical-gene interaction data to systematically predict environmental chemicals associated with disease. We derived chemical-gene signatures for 1,338 chemical/environmental chemicals from the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD). We associated these chemical-gene signatures with differentially expressed genes from datasets found in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) through an enrichment test.
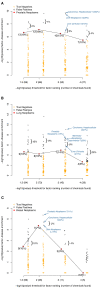
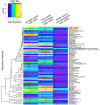
Results: We were able to verify our analytic method by accurately identifying chemicals applied to samples and cell lines. Furthermore, we were able to predict known and novel environmental associations with prostate, lung, and breast cancers, such as estradiol and bisphenol A.
Conclusions: We have developed a scalable and statistical method to identify possible environmental associations with disease using publicly available data and have validated some of the associations in the literature.
Figures

References
-
- Schwartz D, Collins F. Medicine. Environmental biology and human disease. Science. 2007;316(5825):695–696. - PubMed

