Characterization of adipocyte differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells in bone marrow
- PMID: 20459638
- PMCID: PMC2881898
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-10-47
Characterization of adipocyte differentiation from human mesenchymal stem cells in bone marrow
Abstract
Background: Adipocyte hyperplasia is associated with obesity and arises due to adipogenic differentiation of resident multipotent stem cells in the vascular stroma of adipose tissue and remote stem cells of other organs. The mechanistic characterization of adipocyte differentiation has been researched in murine pre-adipocyte models (i.e. 3T3-L1 and 3T3-F442A), revealing that growth-arrest pre-adipocytes undergo mitotic clonal expansion and that regulation of the differentiation process relies on the sequential expression of three key transcription factors (C/EBPbeta, C/EBPalpha and PPARgamma). However, the mechanisms underlying adipocyte differentiation from multipotent stem cells, particularly human mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs), remain poorly understood. This study investigated cell cycle regulation and the roles of C/EBPbeta, C/EBPalpha and PPARgamma during adipocyte differentiation from hBMSCs.
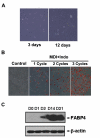
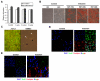
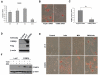
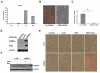
Results: Utilising a BrdU incorporation assay and manual cell counting it was demonstrated that induction of adipocyte differentiation in culture resulted in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes but not hBMSCs undergoing mitotic clonal expansion. Knock-down and over-expression assays revealed that C/EBPbeta, C/EBPalpha and PPARgamma were required for adipocyte differentiation from hBMSCs. C/EBPbeta and C/EBPalpha individually induced adipocyte differentiation in the presence of inducers; PPARgamma alone initiated adipocyte differentiation but the cells failed to differentiate fully. Therefore, the roles of these transcription factors during human adipocyte differentiation are different from their respective roles in mouse.
Conclusions: The characteristics of hBMSCs during adipogenic differentiation are different from those of murine cells. These findings could be important in elucidating the mechanisms underlying human obesity further.
Figures

References
-
- Shepherd PR, Gnudi L, Tozzo E, Yang H, Leach F, Kahn BB. Adipose cell hyperplasia and enhanced glucose disposal in transgenic mice overexpressing GLUT4 selectively in adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:22243–22246. - PubMed
-
- Yu ZK, Wright JT, Hausman GJ. Preadipocyte recruitment in stromal vascular cultures after depletion of committed preadipocytes by immunocytotoxicity. Obesity Res. 1997;5:9–15. - PubMed
-
- Crisan M, Yap S, Casteilla L, Chen CW, Corselli M, Park TS, Andriolo G, Sun B, Zheng B, Zhang L, Norotte C, Teng PN, Traas J, Schugar R, Deasy BM, Badylak S, Buhring HJ, Giacobino JP, Lazzari L, Huard J, Pe'ault B. A Perivascular Origin for Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Multiple Human Organs. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3:301–313. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.07.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

