Diabetes prediction, lipid accumulation product, and adiposity measures; 6-year follow-up: Tehran lipid and glucose study
- PMID: 20459710
- PMCID: PMC2876156
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-45
Diabetes prediction, lipid accumulation product, and adiposity measures; 6-year follow-up: Tehran lipid and glucose study
Abstract
Background: The body mass index (BMI) is the most commonly used marker for evaluating obesity related risks, however, central obesity measures have been proposed to be more informative. Lipid accumulation product (LAP) is an alternative continuous index of lipid accumulation, which is computed from waist circumference (WC, cm) and triglycerides (TGs, mmol/l): (WC-65) xTG (men) and (WC-58) xTG (women). We sought in this study to assess if LAP can outperform BMI, waist-to-height-ratio (WHtR), or waist-to-hip-ratio (WHpR) in identifying prevalent and predicting incident diabetes.
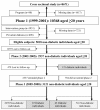
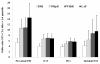
Results: The cross-sectional analyses were performed on a sample included 3,682 men and 4,989 women who were not pregnant, aged > or = 20 years. According to the age (> or = 50 and <50 years) - and sex-specific analyses, odds ratios (ORs) of LAP for prevalent diabetes were higher than those of BMI, WHpR, or WHtR among women, after adjustment for mean arterial pressure and family history of diabetes. The OR of LAP in old men was lower than those of other adiposity measures; in young men, however, LAP was superior to BMI but identical to WHpR and WHtR in identifying prevalent diabetes. Except in young men, LAP showed highest area under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AROC) for prevalent diabetes (P for trend < or = 0.005). For longitudinal analyses, a total of 5,018 non-diabetic subjects were followed for approximately 6 years. The ORs of BMI, WHpR, and WHtR were the same as those of LAP in both sexes and across age groups; except in young men where LAP was superior to the BMI. AROCs of LAP were relatively the same as anthropometric adiposity measures.
Conclusions: LAP was a strong predictor of diabetes and in young individuals had better predictability than did BMI; it was, however, similar to WHpR and WHtR in prediction of incident diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive performances of lipid accumulation product vs. adiposity measures for cardiovascular diseases and all-cause mortality, 8.6-year follow-up: Tehran lipid and glucose study.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Sep 16;9:100. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-100. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20846382 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
References of anthropometric indices of central obesity and metabolic syndrome in Jordanian men and women.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2012 Jan-Mar;6(1):15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2012.05.012. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2012. PMID: 23014249
-
Anthropometric indices predicting incident type 2 diabetes in an Iranian population: the Isfahan Cohort Study.Diabetes Metab. 2013 Oct;39(5):424-31. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Jul 15. Diabetes Metab. 2013. PMID: 23867722
-
A Systematic Review on the Association between Lipid Accumulation Product Index and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2019;34(1):16-20. doi: 10.15605/jafes.034.01.04. Epub 2019 May 28. J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc. 2019. PMID: 33442132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of lipid accumulation product with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Aug 30;21(2):1943-1973. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01114-z. eCollection 2022 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 36404835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The predictive effect of body mass index on type 2 diabetes in the Norwegian women and cancer study.Lipids Health Dis. 2014 Oct 24;13:164. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-13-164. Lipids Health Dis. 2014. PMID: 25344292 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of visceral adiposity index for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 15-year prospective cohort study.Herz. 2015 May;40 Suppl 3:277-81. doi: 10.1007/s00059-014-4175-1. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Herz. 2015. PMID: 25410470
-
Comparison of obesity indices and triglyceride glucose-related parameters to predict type 2 diabetes mellitus among normal-weight elderly in China.Eat Weight Disord. 2022 Apr;27(3):1181-1191. doi: 10.1007/s40519-021-01238-w. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Eat Weight Disord. 2022. PMID: 34195936
-
Fatty Liver Index and Lipid Accumulation Product Can Predict Metabolic Syndrome in Subjects without Fatty Liver Disease.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017;2017:9279836. doi: 10.1155/2017/9279836. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017. PMID: 28194177 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and lipid-related parameters for predicting metabolic syndrome in Chinese elderly population.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Dec 20;17(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0927-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30572889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kahn HS, Cheng YJ, Thompson TJ, Imperatore G, Gregg EW. Two Risk-Scoring Systems for Predicting Incident Diabetes Mellitus in U.S. Adults Age 45 to 64 Years. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150:741–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

