Analysis of gene evolution and metabolic pathways using the Candida Gene Order Browser
- PMID: 20459735
- PMCID: PMC2880306
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-290
Analysis of gene evolution and metabolic pathways using the Candida Gene Order Browser
Abstract
Background: Candida species are the most common cause of opportunistic fungal infection worldwide. Recent sequencing efforts have provided a wealth of Candida genomic data. We have developed the Candida Gene Order Browser (CGOB), an online tool that aids comparative syntenic analyses of Candida species. CGOB incorporates all available Candida clade genome sequences including two Candida albicans isolates (SC5314 and WO-1) and 8 closely related species (Candida dubliniensis, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, Lodderomyces elongisporus, Debaryomyces hansenii, Pichia stipitis, Candida guilliermondii and Candida lusitaniae). Saccharomyces cerevisiae is also included as a reference genome.
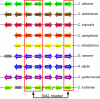
Results: CGOB assignments of homology were manually curated based on sequence similarity and synteny. In total CGOB includes 65617 genes arranged into 13625 homology columns. We have also generated improved Candida gene sets by merging/removing partial genes in each genome. Interrogation of CGOB revealed that the majority of tandemly duplicated genes are under strong purifying selection in all Candida species. We identified clusters of adjacent genes involved in the same metabolic pathways (such as catabolism of biotin, galactose and N-acetyl glucosamine) and we showed that some clusters are species or lineage-specific. We also identified one example of intron gain in C. albicans.
Conclusions: Our analysis provides an important resource that is now available for the Candida community. CGOB is available at http://cgob.ucd.ie.
Figures





References
-
- Jeffries TW, Grigoriev IV, Grimwood J, Laplaza JM, Aerts A, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Lindquist E, Dehal P, Shapiro H, Jin YS, Passoth V, Richardson PM. Genome sequence of the lignocellulose-bioconverting and xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:319–326. doi: 10.1038/nbt1290. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dujon B, Sherman D, Fischer G, Durrens P, Casaregola S, Lafontaine I, De Montigny J, Marck C, Neuveglise C, Talla E, Goffard N, Frangeul L, Aigle M, Anthouard V, Babour A, Barbe V, Barnay S, Blanchin S, Beckerich JM, Beyne E, Bleykasten C, Boisrame A, Boyer J, Cattolico L, Confanioleri F, De Daruvar A, Despons L, Fabre E, Fairhead C, Ferry-Dumazet H, Groppi A, Hantraye F, Hennequin C, Jauniaux N, Joyet P, Kachouri R, Kerrest A, Koszul R, Lemaire M, Lesur I, Ma L, Muller H, Nicaud JM, Nikolski M, Oztas S, Ozier-Kalogeropoulos O, Pellenz S, Potier S, Richard GF, Straub ML, Suleau A, Swennen D, Tekaia F, Wesolowski-Louvel M, Westhof E, Wirth B, Zeniou-Meyer M, Zivanovic I, Bolotin-Fukuhara M, Thierry A, Bouchier C, Caudron B, Scarpelli C, Gaillardin C, Weissenbach J, Wincker P, Souciet JL. Genome evolution in yeasts. Nature. 2004;430:35–44. doi: 10.1038/nature02579. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Butler G, Rasmussen MD, Lin MF, Santos MA, Sakthikumar S, Munro CA, Rheinbay E, Grabherr M, Forche A, Reedy JL, Agrafioti I, Arnaud MB, Bates S, Brown AJ, Brunke S, Costanzo MC, Fitzpatrick DA, de Groot PW, Harris D, Hoyer LL, Hube B, Klis FM, Kodira C, Lennard N, Logue ME, Martin R, Neiman AM, Nikolaou E, Quail MA, Quinn J, Santos MC, Schmitzberger FF, Sherlock G, Shah P, Silverstein KA, Skrzypek MS, Soll D, Staggs R, Stansfield I, Stumpf MP, Sudbery PE, Srikantha T, Zeng Q, Berman J, Berriman M, Heitman J, Gow NA, Lorenz MC, Birren BW, Kellis M, Cuomo CA. Evolution of pathogenicity and sexual reproduction in eight Candida genomes. Nature. 2009;4;459(7247):657–62. doi: 10.1038/nature08064. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

