Antitumor and antiangiogenic effect of the dual EGFR and HER-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib in a lung cancer model
- PMID: 20459769
- PMCID: PMC2883966
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-188
Antitumor and antiangiogenic effect of the dual EGFR and HER-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib in a lung cancer model
Abstract
Background: There is strong evidence demonstrating that activation of epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFRs) leads to tumor growth, progression, invasion and metastasis. Erlotinib and gefitinib, two EGFR-targeted agents, have been shown to be relevant drugs for lung cancer treatment. Recent studies demonstrate that lapatinib, a dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor of EGFR and HER-2 receptors, is clinically effective against HER-2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. In this report, we investigated the activity of lapatinib against non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: We selected the lung cancer cell line A549, which harbors genomic amplification of EGFR and HER-2. Proliferation, cell cycle analysis, clonogenic assays, and signaling cascade analyses (by western blot) were performed in vitro. In vivo experiments with A549 cells xenotransplanted into nude mice treated with lapatinib (with or without radiotherapy) were also carried out.
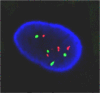
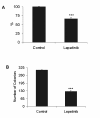
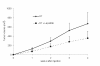
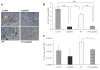
Results: Lapatinib dramatically reduced cell proliferation (P < 0.0001), DNA synthesis (P < 0.006), and colony formation capacity (P < 0.0001) in A549 cells in vitro. Furthermore, lapatinib induced G1 cell cycle arrest (P < 0.0001) and apoptotic cell death (P < 0.0006) and reduced cyclin A and B1 levels, which are regulators of S and G2/M cell cycle stages, respectively. Stimulation of apoptosis in lapatinib-treated A549 cells was correlated with increased cleaved PARP, active caspase-3, and proapoptotic Bak-1 levels, and reduction in the antiapoptotic IAP-2 and Bcl-xL protein levels. We also demonstrate that lapatinib altered EGFR/HER-2 signaling pathways reducing p-EGFR, p-HER-2, p-ERK1/2, p-AKT, c-Myc and PCNA levels. In vivo experiments revealed that A549 tumor-bearing mice treated with lapatinib had significantly less active tumors (as assessed by PET analysis) (P < 0.04) and smaller in size than controls. In addition, tumors from lapatinib-treated mice showed a dramatic reduction in angiogenesis (P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Overall, these data suggest that lapatinib may be a clinically useful agent for the treatment of lung cancer.
Figures
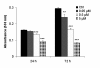


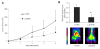
References
-
- Pajares MJ, Zudaire I, Lozano MD, Agorreta J, Bastarrika G, Torre W, Remirez A, Pio R, Zulueta JJ, Montuenga LM. Molecular profiling of computed tomography screen-detected lung nodules shows multiple malignant features. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:373–380. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0320. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, Porta R, Cardenal F, Camps C, Majem M, Lopez-Vivanco G, Isla D, Provencio M, Insa A, Massuti B, Gonzalez-Larriba JL, Paz-Ares L, Bover I, Garcia-Campelo R, Moreno MA, Catot S, Rolfo C, Reguart N, Palmero R, Sánchez JM, Bastus R, Mayo C, Bertran-Alamillo J, Molina MA, Sanchez JJ, Taron M. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:958–967. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0904554. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rocha-Lima CM, Soares HP, Raez LE, Singal R. EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control. 2007;14:295–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

