The SPARK Study: a phase II randomized blinded controlled trial of the effect of furosemide in critically ill patients with early acute kidney injury
- PMID: 20459801
- PMCID: PMC2874544
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-11-50
The SPARK Study: a phase II randomized blinded controlled trial of the effect of furosemide in critically ill patients with early acute kidney injury
Abstract
Background: Furosemide is commonly prescribed in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury (AKI). Existing data from observational studies and small clinical trials have significant limitations and have reported conflicting findings. There remains controversy on whether furosemide can impact clinical outcomes in critically ill patients with AKI; however, a survey of intensivists and nephrologists showed equipoise for high-quality evidence on this important issue.
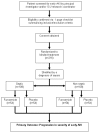
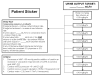
Design/methods: This protocol summarizes the rationale and design of a phase II randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial of a low-dose continuous infusion of furosemide, titrated to the physiology parameter of urine output, in critically ill patients with early AKI. Two hundred sixteen adult critically ill patients with early evidence of AKI, defined by the RIFLE criteria, will be enrolled. Included patients will also have fulfilled >or=2 criteria of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and achieved immediate goals of acute resuscitation. The primary outcome is progression in severity of kidney injury. Secondary outcomes include: safety, fluid balance, electrolyte balance, the need for renal replacement therapy, duration of AKI, rate of renal recovery, mortality and changes in novel serum and urine biomarkers of AKI. The primary analysis will be intention-to-treat. Planned recruitment will be complete by June 2011 and results available by December 2011.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier NCT00978354.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trial of Furosemide to Prevent Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial.Indian J Pediatr. 2021 Nov;88(11):1099-1106. doi: 10.1007/s12098-021-03727-3. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Indian J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33796993 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of low-dose furosemide in critically ill patients with early acute kidney injury: A pilot randomized blinded controlled trial (the SPARK study).J Crit Care. 2017 Dec;42:138-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.07.030. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28732314 Clinical Trial.
-
Association between furosemide administration and outcomes in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury.Crit Care. 2020 Mar 4;24(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-2798-6. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32131879 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Infusion versus Intermittent Bolus Injection of Furosemide in Critically Ill Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018 Oct;32(5):2303-2310. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018. PMID: 29454528
-
Furosemide as a functional marker of acute kidney injury in ICU patients: a new role for an old drug.J Nephrol. 2019 Dec;32(6):883-893. doi: 10.1007/s40620-019-00614-1. Epub 2019 May 14. J Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31090022 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiology and management of septic acute kidney injury.Pediatr Nephrol. 2014 Jan;29(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s00467-013-2427-6. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 23400860 Review.
-
Classification and staging of acute kidney injury: beyond the RIFLE and AKIN criteria.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011 Apr;7(4):201-8. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.14. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21364520 Review.
-
Intermittent furosemide administration in patients with or at risk for acute kidney injury: Meta-analysis of randomized trials.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 24;13(4):e0196088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196088. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29689116 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Trial of Furosemide to Prevent Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial.Indian J Pediatr. 2021 Nov;88(11):1099-1106. doi: 10.1007/s12098-021-03727-3. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Indian J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33796993 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Permissive hypofiltration: an alternative view.Crit Care. 2012 Nov 8;16(6):458. doi: 10.1186/cc11494. Crit Care. 2012. PMID: 23136903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C. Beginning and Ending Supportive Therapy for the Kidney (BEST Kidney) Investigators. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–818. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.7.813. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Laupland KB, Doig CJ, Mortis G, Fick GH, Mucenski M, Godinez-Luna T, Svenson LW, Rosenal T. Prognosis for long-term survival and renal recovery in critically ill patients with severe acute renal failure: a population-based study. Crit Care. 2005;9:R700–R709. doi: 10.1186/cc3879. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical