Altered microRNA expression profile with miR-146a upregulation in CD4+ T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20459811
- PMCID: PMC2911863
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3006
Altered microRNA expression profile with miR-146a upregulation in CD4+ T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Increasing evidence indicates that microRNAs (miRNAs) play a critical role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. The aim of the study was to investigate the expression pattern and function of miRNAs in CD4+ T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
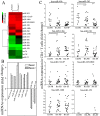
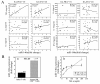
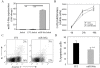
Methods: The expression profile of miRNAs in CD4+ T cells from synovial fluid (SF) and peripheral blood of 33 RA patients was determined by microarray assay and validated by qRT-PCR analysis. The correlation between altered expression of miRNAs and cytokine levels was determined by linear regression analysis. The role of miR-146a overexpression in regulating T cell apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry. A genome-wide gene expression analysis was further performed to identify miR-146a-regulated genes in T cells.
Results: miRNA expression profile analysis revealed that miR-146a expression was significantly upregulated while miR-363 and miR-498 were downregulated in CD4+ T cells of RA patients. The level of miR-146a expression was positively correlated with levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), and in vitro studies showed TNF-alpha upregulated miR-146a expression in T cells. Moreover, miR-146a overexpression was found to suppress Jurkat T cell apoptosis. Finally, transcriptome analysis of miR-146a overexpression in T cells identified Fas associated factor 1 (FAF1) as a miR-146a-regulated gene, which was critically involved in modulating T cell apoptosis.
Conclusions: We have detected increased miR-146a in CD4+ T cells of RA patients and its close correlation with TNF-alpha levels. Our findings that miR-146a overexpression suppresses T cell apoptosis indicate a role of miR-146a in RA pathogenesis and provide potential novel therapeutic targets.
Figures

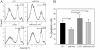
Comment in
-
Biomarkers: microRNAs under the spotlight in inflammatory arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 Aug;6(8):436. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.112. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20704032 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ali M, Ponchel F, Wilson KE, Francis MJ, Wu X, Verhoef A, Boylston AW, Veale DJ, Emery P, Markham AF, Lamb JR, Isaacs JD. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial T cells regulate transcription of several genes associated with antigen-induced anergy. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:519–528. doi: 10.1172/JCI8027. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

