eHive: an artificial intelligence workflow system for genomic analysis
- PMID: 20459813
- PMCID: PMC2885371
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-240
eHive: an artificial intelligence workflow system for genomic analysis
Abstract
Background: The Ensembl project produces updates to its comparative genomics resources with each of its several releases per year. During each release cycle approximately two weeks are allocated to generate all the genomic alignments and the protein homology predictions. The number of calculations required for this task grows approximately quadratically with the number of species. We currently support 50 species in Ensembl and we expect the number to continue to grow in the future.
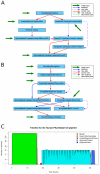
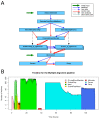
Results: We present eHive, a new fault tolerant distributed processing system initially designed to support comparative genomic analysis, based on blackboard systems, network distributed autonomous agents, dataflow graphs and block-branch diagrams. In the eHive system a MySQL database serves as the central blackboard and the autonomous agent, a Perl script, queries the system and runs jobs as required. The system allows us to define dataflow and branching rules to suit all our production pipelines. We describe the implementation of three pipelines: (1) pairwise whole genome alignments, (2) multiple whole genome alignments and (3) gene trees with protein homology inference. Finally, we show the efficiency of the system in real case scenarios.
Conclusions: eHive allows us to produce computationally demanding results in a reliable and efficient way with minimal supervision and high throughput. Further documentation is available at: http://www.ensembl.org/info/docs/eHive/.
Figures



References
-
- Hubbard TJ, Aken BL, Ayling S, Ballester B, Beal K, Bragin E, Brent S, Chen Y, Clapham P, Clarke L, Coates G, Fairley S, Fitzgerald S, Fernandez-Banet J, Gordon L, Graf S, Haider S, Hammond M, Holland R, Howe K, Jenkinson A, Johnson N, Kahari A, Keefe D, Keenan S, Kinsella R, Kokocinski F, Kulesha E, Lawson D, Longden I, Megy K, Meidl P, Overduin B, Parker A, Pritchard B, Rios D, Schuster M, Slater G, Smedley D, Spooner W, Spudich G, Trevanion S, Vilella A, Vogel J, White S, Wilder S, Zadissa A, Birney E, Cunningham F, Curwen V, Durbin R, Fernandez-Suarez XM, Herrero J, Kasprzyk A, Proctor G, Smith J, Searle S, Flicek P. Ensembl 2009. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37:D690–D697. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn828. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reynolds CW. Flocks, herds and schools: A distributed behavioral model. Proceedings of the 14th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 1987. pp. 25–34. full_text.
-
- Nii HP. The blackboard model of problem solving and the evolution of blackboard architectures. AI Magazine. 1986;7:38–53.
-
- Nwana HS. Software agents: An overview. Knowledge Engineering Review. 1996;11:205–244. doi: 10.1017/S026988890000789X. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

