New insights into the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton by tropomyosin
- PMID: 20460184
- PMCID: PMC2923581
- DOI: 10.1016/S1937-6448(10)81003-2
New insights into the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton by tropomyosin
Abstract
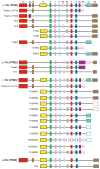
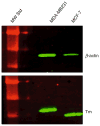
The actin cytoskeleton is regulated by a variety of actin-binding proteins including those constituting the tropomyosin family. Tropomyosins are coiled-coil dimers that bind along the length of actin filaments. In muscles, tropomyosin regulates the interaction of actin-containing thin filaments with myosin-containing thick filaments to allow contraction. In nonmuscle cells where multiple tropomyosin isoforms are expressed, tropomyosins participate in a number of cellular events involving the cytoskeleton. This chapter reviews the current state of the literature regarding tropomyosin structure and function and discusses the evidence that tropomyosins play a role in regulating actin assembly.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
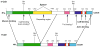
References
-
- Alahyan M, Webb MR, Marston SB, El-Mezgueldi M. The mechanism of smooth muscle caldesmon–tropomyosin inhibition of the elementary steps of the acto-myosin ATPase. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:19433–19448. - PubMed
-
- Ansari S, Alahyan M, Marston SB, El-Mezgueldi M. Role of caldesmon in the Ca2+ regulation of smooth muscle thin filaments: evidence for a cooperative switching mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:47–56. - PubMed
-
- Beisel KW, Kennedy JE. Identification of novel alternatively spliced isoforms of the tropomyosin-encoding gene, TMnm, in the rat cochlea. Gene. 1994;143:251–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

