MRI findings of primary CNS lymphoma in 26 immunocompetent patients
- PMID: 20461180
- PMCID: PMC2864853
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.3.269
MRI findings of primary CNS lymphoma in 26 immunocompetent patients
Abstract
Objective: To record the MR imaging features of primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) and compare these features in monofocal and multifocal disease.
Materials and methods: Twenty-one cases of monofocal disease were compared to five cases of multifocal disease. All patients were examined by non-enhanced and contrast-enhanced MRI. Tumor location, tumor size, signal intensity, enhancement characteristics, age distribution, peritumoral edema, cystic changes, and the presence of calcifications were assessed. The MRI features were compared between the monofocal and multifocal disease cases.
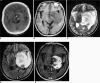
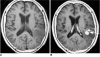
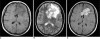
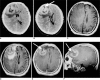
Results: The 26 cases, including both the monofocal and multifocal cases, exhibited 37 lesions. Contrast-enhanced images showed variable enhancement patterns: homogeneous enhancement (33 lesions), ring-like enhancement (2), and 'open-ring-like' enhancement (2). The 'notch sign' was noted in four of 33 homogeneously enhancing lesions. One case of hemorrhage and three cases of cystic formation were observed. Intra-tumoral calcification was not found. The frontal lobe, the corpus callosum and the basal ganglia were commonly affected in both the monofocal and multifocal groups. Tumor size differed significantly between the two groups (t = 3.129, p < 0.01) and mildly or moderately enhanced lesions were more frequently found in the monofocal group (p < 0.05). There was no statistical difference between perifocal edema (p > 0.05) and the signal characteristics (p > 0.05) between the two groups.
Conclusion: Our data show that PCNSL has a variable enhancement pattern on MR images. We first reported two lesions with an 'open-ring' enhancement as well as four cases with a 'notch sign'. Monofocal PCNSL cases typically have larger sized tumors with mild or moderate enhancement.
Keywords: Brain neoplasm; Computed tomography (CT); Lymphoma; Magnetic resonance (MR).
Figures
Comment in
-
Correspondence re: MRI findings of primary CNS lymphoma in 26 immunocompetent patients.Korean J Radiol. 2010 Nov-Dec;11(6):702-3. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.6.702. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Korean J Radiol. 2010. PMID: 21076600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Primary central nervous system lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: a retrospective review of MRI features.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2012 Jun;56(3):295-301. doi: 10.1111/j.1754-9485.2012.02366.x. Epub 2012 Apr 10. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22697326 Review.
-
Clinical Significance of Discrepancy between Arterial Spin Labeling Images and Contrast-enhanced Images in the Diagnosis of Brain Tumors.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2015;14(4):313-9. doi: 10.2463/mrms.2014-0083. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26104074
-
Magnetic resonance findings of primary central nervous system T-cell lymphoma in immunocompetent patients.Acta Radiol. 2005 Apr;46(2):187-92. doi: 10.1080/02841850510022714. Acta Radiol. 2005. PMID: 15902895
-
New MR perfusion features in primary central nervous system lymphomas: pattern and prognostic impact.J Neurol. 2018 Mar;265(3):647-658. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-8737-7. Epub 2018 Jan 30. J Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29383512
-
Neuroimaging of primary central nervous system lymphoma in immunocompetent patients: comparison of recent and previous findings.J Nippon Med Sch. 2013;80(3):174-83. doi: 10.1272/jnms.80.174. J Nippon Med Sch. 2013. PMID: 23832401 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary CNS lymphoma of the corpus callosum: presentation and neurocognitive outcomes.J Neurooncol. 2022 May;158(1):99-109. doi: 10.1007/s11060-022-04014-7. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J Neurooncol. 2022. PMID: 35445956
-
A systematic approach to the diagnosis of suspected central nervous system lymphoma.JAMA Neurol. 2013 Mar 1;70(3):311-9. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.606. JAMA Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23319132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values and Conventional MRI Features in Differentiating Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions From Primary Brain Neoplasms.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 Nov;205(5):1075-85. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.13970. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015. PMID: 26496556 Free PMC article.
-
Primary central nervous system lymphoma: is absence of intratumoral hemorrhage a characteristic finding on MRI?Radiol Oncol. 2015 Mar 25;49(2):128-34. doi: 10.1515/raon-2015-0007. eCollection 2015 Jun. Radiol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26029023 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging features (CT, MRI, MRS, and PET/CT) of primary central nervous system lymphoma in immunocompetent patients.Neurol Sci. 2019 Mar;40(3):535-542. doi: 10.1007/s10072-018-3669-7. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30580380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gutmann J, Kendall B. Unusual appearances of primary central nervous system non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clin Radiol. 1994;49:696–702. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Takeda N, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H. Correlation of computed tomography with the histopathology of primary malignant lymphoma of the brain. Neuroradiology. 1992;34:36–42. - PubMed
-
- Coulon A, Lafitte F, Hoang-Xuan K, Martin-Duverneuil N, Mokhtari K, Blustajn J, et al. Radiographic findings in 37 cases of primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients. Eur Radiol. 2002;12:329–340. - PubMed
-
- Miller DC, Hochberg FH, Harris NL, Gruber ML, Louis DN, Cohen H. Pathology with clinical correlations of primary central nervous system non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The Massachusetts General Hospital experience 1958-1989. Cancer. 1994;74:1383–1397. - PubMed
-
- Nitta T, Uda K, Ebato M, Ikezaki K, Fukui M, Sato K. Primary peripheral-postthymic T-cell lymphoma in the central nervous system: immunological and molecular approaches to diagnosis. J Neurosurg. 1995;82:77–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

