Protection by Chrysanthemum zawadskii extract from liver damage of mice caused by carbon tetrachloride is maybe mediated by modulation of QR activity
- PMID: 20461196
- PMCID: PMC2867229
- DOI: 10.4162/nrp.2010.4.2.93
Protection by Chrysanthemum zawadskii extract from liver damage of mice caused by carbon tetrachloride is maybe mediated by modulation of QR activity
Abstract
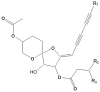
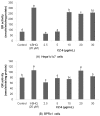
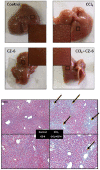
Our previous study demonstrated that methanolic extract of Chrysanthemum zawadskii Herbich var. latilobum Kitamura (Compositae) has the potential to induce detoxifying enzymes such as NAD(P)H:(quinone acceptor) oxidoreductase 1 (EC 1.6.99.2) (NQO1, QR) and glutathione S-transferase (GST). In this study we further fractionated methanolic extract of Chrysanthemum zawadskii and investigated the detoxifying enzyme-inducing potential of each fraction. The fraction (CZ-6) shown the highest QR-inducing activity was found to contain (+)-(3S,4S,5R,8S)-(E)-8-acetoxy-4-hydroxy-3-isovaleroyloxy-2-(hexa-2,4-diynyliden)-1,6-dioxaspiro [4,5] decane and increased QR enzyme activity in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, CZ-6 fraction caused a dose-dependent enhancement of luciferase activity in HepG2-C8 cells generated by stably transfecting antioxidant response element-luciferase gene construct, suggesting that it induces antioxidant/detoxifying enzymes through antioxidant response element (ARE)-mediated transcriptional activation of the relevant genes. Although CZ-6 fraction failed to induce hepatic QR in mice over the control, it restored QR activity suppressed by CCl(4) treatment to the control level. Hepatic injury induced by CCl(4) was also slightly protected by pretreatment with CZ-6. In conclusion, although CZ-6 fractionated from methanolic extract of Chrysanthemum zawadskii did not cause a significant QR induction in mice organs such as liver, kidney, and stomach, it showed protective effect from liver damage caused by CCl(4).
Keywords: (+)-(3S,4S,5R,8S)-(E)-8-acetoxy-4-hydroxy-3-isovaleroyloxy-2-(hexa-2,4-diynyliden)-1,6-dioxaspiro[4,5]decane; Chrysanthemum zawadskii; Quinone reductase; carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury; detoxifying enzymes.
Figures
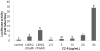
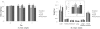
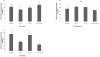
References
-
- Kwon HS, Ha TJ, Hwang SW, Jin YM, Nam SH, Park KH, Yang MS. Cytotoxic flavonoids from the whole plants of Chrysanthemum zawadskii Herbich var. latilobum Kitamura. J Life Sci. 2006;16:746–749.
-
- Kang HS, Park MJ, Jin KS, Kim YH, Jun M, Lim HJ, Jo WK, Kim JS, Jeong WS. Regulatory roles of Chrysanthemum zawadskii roots in nuclear factor E2-related factor 2/antioxidant response element pathway. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2008;17:367–372.
-
- Kim JR, Kim JH, Lim HA, Jang CH, Kim JH, Kwon CS, Kim YK, Kim JS. Induction of quinone reductase, an anticarcinogenic marker enzyme, by extract from Chrysanthemum zawadskii var. latilobum K. Journal of Food Science and Nutrition. 2005;10:340–343.
-
- Mehta RG, Pezzuto JM. Discovery of cancer preventive agents from natural products: from plants to prevention. Curr Oncol Rep. 2002;4:478–486. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

