Bimodal expression of Sprouty2 during the cell cycle is mediated by phase-specific Ras/MAPK and c-Cbl activities
- PMID: 20461437
- PMCID: PMC11115549
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0379-6
Bimodal expression of Sprouty2 during the cell cycle is mediated by phase-specific Ras/MAPK and c-Cbl activities
Abstract
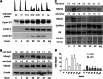
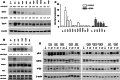
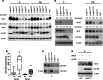
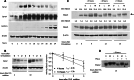
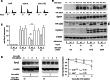
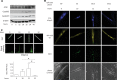
Sprouty2 is an important inhibitor of cell proliferation and signal transduction. In this study, we found a bimodal expression of Sprouty2 protein during cell cycle progression after exit from quiescence, whereas elevated Sprouty4 expression in the G1 phase stayed high throughout the rest of the cell cycle. Induction of the mitogen-activated protein kinase via activated Ras was crucial for increased Sprouty2 expression at the G0/G1 transition. Following the first peak, accelerated proteasomal protein degradation caused a transient attenuation of Sprouty2 abundance during late G1. Since the decline in its expression was abolished by dominant negative c-Cbl and the timely restricted interaction between Sprouty2 and c-Cbl disappeared at the second peak of Sprouty2 expression, we conclude that the second phase in the cell cycle-specific expression profile of Sprouty2 is solely dependent on ubiquitination by c-Cbl. Our results suggest that Sprouty2 abundance is the result of strictly coordinated activities of Ras and c-Cbl.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation of Sprouty proteins regulates their ability to inhibit growth factor signaling: a dual feedback loop.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 May;15(5):2176-88. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-07-0503. Epub 2004 Mar 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. Retraction in: Mol Biol Cell. 2022 Jul 1;33(8):re3. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E03-07-0503-corr. PMID: 15004239 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Sprouty2 acts at the Cbl/CIN85 interface to inhibit epidermal growth factor receptor downregulation.EMBO Rep. 2005 Jul;6(7):635-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400453. EMBO Rep. 2005. PMID: 15962011 Free PMC article.
-
[Changes in the activity of cyclin-kinase complexes governing cell transition from G1 phase to DNA replication phase in E1A + c-Ha-ras transformants transfected with the bcl-2 gene].Tsitologiia. 2003;45(2):149-57. Tsitologiia. 2003. PMID: 12722479 Russian.
-
Identification of a dominant negative mutant of Sprouty that potentiates fibroblast growth factor- but not epidermal growth factor-induced ERK activation.J Biol Chem. 2001 Sep 28;276(39):36804-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100386200. Epub 2001 Aug 8. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11495895
-
The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway.J Thorac Oncol. 2006 Jan;1(1):7-9. J Thorac Oncol. 2006. PMID: 17409820 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A Sprouty4 Mutation Identified in Kallmann Syndrome Increases the Inhibitory Potency of the Protein towards FGF and Connected Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 21;22(4):2145. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042145. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670044 Free PMC article.
-
Sprouty4 interferes with cell proliferation and migration of breast cancer-derived cell lines.Tumour Biol. 2014 May;35(5):4447-56. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-1587-0. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 24402575
-
The role of CBL family ubiquitin ligases in cancer progression and therapeutic strategies.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 26;15:1432545. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1432545. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39130630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sprouty3, but Not Sprouty1, Expression Is Beneficial for the Malignant Potential of Osteosarcoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 4;22(21):11944. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111944. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769378 Free PMC article.
-
Sprouty3 and Sprouty4, Two Members of a Family Known to Inhibit FGF-Mediated Signaling, Exert Opposing Roles on Proliferation and Migration of Glioblastoma-Derived Cells.Cells. 2019 Aug 1;8(8):808. doi: 10.3390/cells8080808. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31374860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minowada G, Jarvis LA, Chi CL, Neubuser A, Sun X, Hacohen N, Krasnow MA, Martin GR. Vertebrate Sprouty genes are induced by FGF signaling and can cause chondrodysplasia when overexpressed. Development. 1999;126:4465–4475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

