Phase II study of sunitinib as second-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 20461441
- PMCID: PMC3171673
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-010-9438-y
Phase II study of sunitinib as second-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
Purpose: This phase II, open-label, multicenter study assessed the oral, multitargeted, tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib in patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma who had received prior chemotherapy.
Experimental design: Patients received sunitinib 50 mg/day on Schedule 4/2 (4 weeks on treatment, followed by 2 weeks off treatment). The primary endpoint was objective response rate; secondary endpoints included clinical benefit rate, duration of response, progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability, and quality of life.
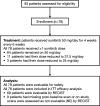
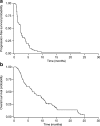
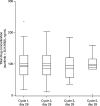
Results: Of 78 patients enrolled, most had gastric adenocarcinoma (93.6%) and metastatic disease (93.6%). All were evaluable for safety and efficacy. Two patients (2.6%) had partial responses and 25 patients (32.1%) had a best response of stable disease for ≥6 weeks. Median PFS was 2.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6-2.6 months) and median OS was 6.8 months (95% CI, 4.4-9.6 months). Grade ≥ 3 thrombocytopenia and neutropenia were reported in 34.6% and 29.4% of patients, respectively, and the most common non-hematologic adverse events were fatigue, anorexia, nausea, diarrhea, and stomatitis. Pharmacokinetics of sunitinib and its active metabolite were consistent with previous reports. There were no marked associations between baseline soluble protein levels, or changes from baseline, and measures of clinical outcome.
Conclusions: The progression-delaying effect and manageable toxicity observed with sunitinib in this study suggest that although single-agent sunitinib has insufficient clinical value as second-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer, its role in combination with chemotherapy merits further study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase II study of sunitinib administered in a continuous once-daily dosing regimen in patients with cytokine-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Sep 1;27(25):4068-75. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.5476. Epub 2009 Aug 3. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19652072 Clinical Trial.
-
Sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.JAMA. 2006 Jun 7;295(21):2516-24. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.21.2516. JAMA. 2006. PMID: 16757724 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized phase II study of sunitinib versus standard of care for patients with previously treated advanced triple-negative breast cancer.Breast. 2013 Oct;22(5):650-6. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2013.07.037. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Breast. 2013. PMID: 23958375 Clinical Trial.
-
Sunitinib malate for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumors.Clin Ther. 2007 Jul;29(7):1338-53. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.07.022. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 17825686 Review.
-
Relationship between exposure to sunitinib and efficacy and tolerability endpoints in patients with cancer: results of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic meta-analysis.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;66(2):357-71. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-1170-y. Epub 2009 Dec 5. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19967539 Review.
Cited by
-
Current status of novel agents in advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015 Feb;6(1):60-74. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2014.098. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25642339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current treatments and outlook in adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction: a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Mar;10(6):377. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1064. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35433931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted therapies for metastatic esophagogastric cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2011 Mar;12(1):46-60. doi: 10.1007/s11864-011-0138-4. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21298375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted therapies in gastric cancer treatment: where we are and where we are going.Invest New Drugs. 2016 Jun;34(3):378-93. doi: 10.1007/s10637-016-0330-2. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Invest New Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26873643 Review.
-
Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Gastric Cancer. State of the Art.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 14;13(16):4094. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164094. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439248 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilson D, Hiller L, Geh JI. Review of second-line chemotherapy for advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2005;17:81–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

