Targeted Sprouty1 overexpression in cardiac myocytes does not alter myocardial remodeling or function
- PMID: 20461448
- PMCID: PMC2923832
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-010-0468-8
Targeted Sprouty1 overexpression in cardiac myocytes does not alter myocardial remodeling or function
Abstract
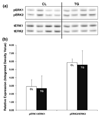
The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway regulates multiple events leading to heart failure including ventricular remodeling, contractility, hypertrophy, apoptosis, and fibrosis. The regulation of conserved intrinsic inhibitors of this pathway is poorly understood. We recently identified an up-regulation of Sprouty1 (Spry1) in a targeted approach for novel inhibitors of the MAPK signaling pathway in failing human hearts following reverse remodeling. The goal of this study was to test the hypothesis that up-regulated expression of Spry1 in cardiac myocytes would be sufficient to inhibit ERK1/2 activation and tissue remodeling. We established a murine model with up-regulated Spry1 expression in cardiac myocytes using the alpha-myosin heavy chain promoter (alpha-MHC). Heart weight and cardiac myocyte morphology were unchanged in adult male alpha-MHC-Spry1 mice compared to control mice. Ventricular function of alpha-MHC-Spry1 mice was unaltered at 8 weeks or 1 year of age. These findings were consistent with the lack of an effect of Spry1 on ERK1/2 activity. In summary, targeted up-regulation of Spry1 in cardiac myocytes is not sufficient to alter cell or tissue remodeling consistent with the lack of an effect on ERK1/2 activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of cardiomyocyte Sprouty1 protects from cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury.Basic Res Cardiol. 2019 Jan 11;114(2):7. doi: 10.1007/s00395-018-0713-y. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30635790 Free PMC article.
-
[Myocardial expression of Spry1 and MAPK proteins of viral myocarditis].Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013 Jun;29(3):164-7. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24303755 Chinese.
-
Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 10 Negatively Regulates Cardiac Remodeling by Blocking Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Extracellular Signal-Regulated Protein Kinase 1/2 Signaling.Hypertension. 2016 Jan;67(1):86-98. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05957. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 26573707 Review.
-
Wnt signaling is critical for maladaptive cardiac hypertrophy and accelerates myocardial remodeling.Hypertension. 2010 Apr;55(4):939-45. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.141127. Epub 2010 Feb 22. Hypertension. 2010. PMID: 20177000
-
Origins of cardiac fibroblasts.Circ Res. 2010 Nov 26;107(11):1304-12. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.231910. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 21106947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of cardiomyocyte Sprouty1 protects from cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury.Basic Res Cardiol. 2019 Jan 11;114(2):7. doi: 10.1007/s00395-018-0713-y. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30635790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heineke J, Molkentin JD. Regulation of cardiac hypertrophy by intracellular signalling pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:589–600. - PubMed
-
- Wohlschlaeger J, Schmitz KJ, Schmid C, Schmid KW, Keul P, Takeda A, Weis S, Levkau B, Baba HA. Reverse remodeling following insertion of left ventricular assist devices LVAD): a review of the morphological and molecular changes. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;68:376–386. - PubMed
-
- Dipla K, Mattiello JA, Jeevanandam V, Houser SR, Margulies KB. Myocyte recovery after mechanical circulatory support in humans with end-stage heart failure. Circulation. 1998;97:2316–2322. - PubMed
-
- Zafeiridis A, Jeevanandam V, Houser SR, Margulies KB. Regression of cellular hypertrophy after left ventricular assist device support. Circulation. 1998;98:656–662. - PubMed
-
- Razeghi P, Bruckner BA, Sharma S, Youker KA, Frazier OH, Taegtmeyer H. Mechanical unloading of the failing human heart fails to activate the protein kinase B/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta survival pathway. Cardiology. 2003;100:17–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

