Inhibition of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C downregulates HER2 overexpression on plasma membrane of breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20462431
- PMCID: PMC2917016
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2575
Inhibition of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C downregulates HER2 overexpression on plasma membrane of breast cancer cells
Abstract
Introduction: Overexpression on plasma membrane of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is reported in 25% to 30% of breast cancers. Heterodimer formation with cognate members of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family, such as HER3 and EGFR, activates abnormal cell-signalling cascades responsible for tumorigenesis and further transcriptional HER2 gene upregulation. Targeting the molecular mechanisms controlling HER2 overexpression and recycling may effectively deactivate this feedback-amplification loop. We recently showed that inactivation of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C (PC-PLC) may exert a pivotal role in selectively modulating the expression on the membrane of specific receptors or proteins relevant to cell function. In the present study, we investigated the capability of PC-PLC inhibition to target the molecular mechanisms controlling HER2 overexpression on the membrane of breast cancer cells by altering the rates of its endocytosis and lysosomal degradation.
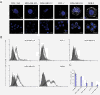
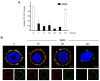
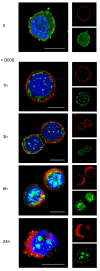
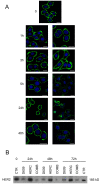
Methods: Localization on the membrane and interaction of PC-PLC with HER2, EGFR, and HER3 were investigated on HER2-overexpressing and HER2-low breast cancer cell lines, by using confocal laser scanning microscopy, flow cytometry, cell-surface biotinylation, isolation of lipid rafts, and immunoprecipitation experiments. The effects of the PC-PLC inhibitor tricyclodecan-9-yl-potassium xanthate (D609) on HER2 expression on the membrane and on the levels of overall HER2, HER2-HER3, and HER2-EGFR contents were monitored in the HER2-overexpressing SKBr3 cells, after either transient or continuous receptor engagement with anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies, including trastuzumab. Changes of HER2 expression and cell proliferation were examined in SKBr3, BT-474, and MDA-MB-453 cells continuously exposed to D609 alone or combined with trastuzumab.
Results: PC-PLC selectively accumulates on the plasma membrane of HER2-overexpressing cells, where it colocalizes and associates with HER2 in raft domains. PC-PLC inhibition resulted in enhanced HER2 internalization and lysosomal degradation, inducing downmodulation of HER2 expression on the membrane. Moreover, PC-PLC inhibition resulted in strong retardation of HER2 reexpression on the membrane and a decrease in the overall cellular contents of HER2, HER2-HER3, and HER2-EGFR heterodimers. The PC-PLC inhibitor also induced antiproliferative effects, especially in trastuzumab-resistant cells.
Conclusions: The results pointed to PC-PLC inhibition as a potential means to counteract the tumorigenic effects of HER2 amplification and complement the effectiveness of current HER2-targeting therapies.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibition of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C results in loss of mesenchymal traits in metastatic breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 19;14(2):R50. doi: 10.1186/bcr3151. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22429397 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C inhibition reduces HER2-overexpression, cell proliferation and in vivo tumor growth in a highly tumorigenic ovarian cancer model.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 5;8(33):55022-55038. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18992. eCollection 2017 Aug 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28903399 Free PMC article.
-
ZD1839, a specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces the formation of inactive EGFR/HER2 and EGFR/HER3 heterodimers and prevents heregulin signaling in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Apr;9(4):1274-83. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12684395
-
Biology of HER2 and its importance in breast cancer.Oncology. 2001;61 Suppl 2:1-13. doi: 10.1159/000055396. Oncology. 2001. PMID: 11694782 Review.
-
Mechanism of action of anti-HER2 monoclonal antibodies: scientific update on trastuzumab and 2C4.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;532:253-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0081-0_21. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003. PMID: 12908564 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and synthesis of phospholipase C and A2-activatable near-infrared fluorescent smart probes.Bioconjug Chem. 2010 Oct 20;21(10):1724-7. doi: 10.1021/bc100271v. Bioconjug Chem. 2010. PMID: 20882956 Free PMC article.
-
Mek activity is required for ErbB2 expression in breast cancer cells detached from the extracellular matrix.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 31;8(62):105383-105396. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22194. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285258 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cancer-specific metabolic pathways for developing novel cancer therapeutics.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 22;13:955476. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.955476. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36618350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidylcholine-Derived Lipid Mediators: The Crosstalk Between Cancer Cells and Immune Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 15;13:768606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.768606. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35250970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tricyclodecan-9-yl-xanthogenate (D609) mechanism of actions: a mini-review of literature.Neurochem Res. 2012 Apr;37(4):671-9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-011-0659-z. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22101393 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lemmon MA. The EGF receptor family as therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Breast Dis. 2003;18:33–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

