Dynamic flexibility of DNA repair pathways in growth arrested Escherichia coli
- PMID: 20462807
- PMCID: PMC2893249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.04.004
Dynamic flexibility of DNA repair pathways in growth arrested Escherichia coli
Abstract
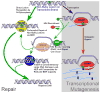
The DNA of all organisms is constantly damaged by exogenous and endogenous agents. Base excision repair (BER) is important for the removal of several non-bulky lesions from the DNA, however not much is known about the contributions of other DNA repair pathways to the processing of non-bulky lesions. Here we utilized a luciferase reporter system to assess the contributions of transcription-coupled repair (TCR), BER and nucleotide excision repair (NER) to the repair of two non-bulky lesions, 8-oxoguanine (8OG) and uracil (U), in vivo under non-growth conditions. We demonstrate that both TCR and NER are utilized by Escherichia coli to repair 8OG and U. Additionally, the relative level of recognition of these lesions by BER and NER suggests that TCR can utilize components of either pathway for lesion removal, depending upon their availability. These findings indicate a dynamic flexibility of DNA repair pathways in the removal of non-bulky DNA lesions in prokaryotes, and reveal their respective contributions to the repair of 8OG and U in vivo.
2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Base excision repair and nucleotide excision repair contribute to the removal of N-methylpurines from active genes.DNA Repair (Amst). 2002 Aug 6;1(8):683-96. doi: 10.1016/s1568-7864(02)00075-7. DNA Repair (Amst). 2002. PMID: 12509290
-
Effects of the bacterial transcription-repair coupling factor during transcription of DNA containing non-bulky lesions.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Oct 1;7(10):1670-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.06.020. Epub 2008 Sep 10. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18707026
-
Excision of Oxidatively Generated Guanine Lesions by Competitive DNA Repair Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 7;22(5):2698. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052698. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33800059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription-coupled global genomic repair in E. coli.Trends Biochem Sci. 2023 Oct;48(10):873-882. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.07.007. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Trends Biochem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37558547 Review.
-
Base and Nucleotide Excision Repair of Oxidatively Generated Guanine Lesions in DNA.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 4;291(10):5309-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693218. Epub 2016 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26733197 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A quantitative assay for assessing the effects of DNA lesions on transcription.Nat Chem Biol. 2012 Oct;8(10):817-22. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1046. Nat Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22902614 Free PMC article.
-
Mfd is required for rapid recovery of transcription following UV-induced DNA damage but not oxidative DNA damage in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2012 May;194(10):2637-45. doi: 10.1128/JB.06725-11. Epub 2012 Mar 16. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22427630 Free PMC article.
-
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Sep;76(3):530-64. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05020-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22933559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase between lesion bypass and DNA repair.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Dec;70(23):4495-509. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1384-3. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23807206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional de-repression and Mfd are mutagenic in stressed Bacillus subtilis cells.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;21(1-2):45-58. doi: 10.1159/000332751. Epub 2012 Jan 13. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22248542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nouspikel T, Hanawalt PC. DNA repair in terminally differentiated cells. DNA Repair. 2002;1:59–75. - PubMed
-
- Hanawalt PC, Spivak G. Transcription-coupled DNA repair: two decades of progress and surprises. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:958–970. - PubMed
-
- Bregeon D, Doddridge ZA, You HJ, Weiss B, Doetsch PW. Transcriptional mutagenesis induced by uracil and 8-oxoguanine in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell. 2003;12:959–970. - PubMed
-
- Grossman L, Lin C, Ahn Y. Nucleotide excision repair. In: Nickoloff J, Hoekstra M, editors. DNA Damage and Repair. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: 1998. pp. 11–27.
-
- Friedberg EC, Walker G, Siede W, Wood RD, Schultz RA, Ellenberger T. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. ASM Press; Washington, D. C.: 2006. DNA damage; pp. 9–70.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

