Distinct contributions of conserved modules to Runt transcription factor activity
- PMID: 20462957
- PMCID: PMC2893994
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-11-0953
Distinct contributions of conserved modules to Runt transcription factor activity
Abstract
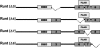
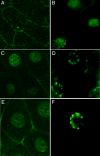
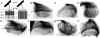
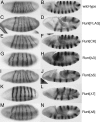
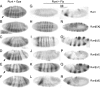
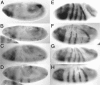
Runx proteins play vital roles in regulating transcription in numerous developmental pathways throughout the animal kingdom. Two Runx protein hallmarks are the DNA-binding Runt domain and a C-terminal VWRPY motif that mediates interaction with TLE/Gro corepressor proteins. A phylogenetic analysis of Runt, the founding Runx family member, identifies four distinct regions C-terminal to the Runt domain that are conserved in Drosophila and other insects. We used a series of previously described ectopic expression assays to investigate the functions of these different conserved regions in regulating gene expression during embryogenesis and in controlling axonal projections in the developing eye. The results indicate each conserved region is required for a different subset of activities and identify distinct regions that participate in the transcriptional activation and repression of the segmentation gene sloppy-paired-1 (slp1). Interestingly, the C-terminal VWRPY-containing region is not required for repression but instead plays a role in slp1 activation. Genetic experiments indicating that Groucho (Gro) does not participate in slp1 regulation further suggest that Runt's conserved C-terminus interacts with other factors to promote transcriptional activation. These results provide a foundation for further studies on the molecular interactions that contribute to the context-dependent properties of Runx proteins as developmental regulators.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evidence That Runt Acts as a Counter-Repressor of Groucho During Drosophila melanogaster Primary Sex Determination.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Jul 7;10(7):2487-2496. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401384. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32457096 Free PMC article.
-
Groucho-dependent and -independent repression activities of Runt domain proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Sep;17(9):5581-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.9.5581. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9271433 Free PMC article.
-
Association with the nuclear matrix and interaction with Groucho and RUNX proteins regulate the transcription repression activity of the basic helix loop helix factor Hes1.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 12;276(2):1578-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007629200. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11035023
-
Groucho/TLE family proteins and transcriptional repression.Gene. 2000 May 16;249(1-2):1-16. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00161-x. Gene. 2000. PMID: 10831834 Review.
-
Runx transcription factors and the developmental balance between cell proliferation and differentiation.Cell Biol Int. 2003;27(4):315-24. doi: 10.1016/s1065-6995(03)00018-0. Cell Biol Int. 2003. PMID: 12788047 Review.
Cited by
-
Different modes of enhancer-specific regulation by Runt and Even-skipped during Drosophila segmentation.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Mar 1;28(5):681-691. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-09-0630. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28077616 Free PMC article.
-
An ancient Pygo-dependent Wnt enhanceosome integrated by Chip/LDB-SSDP.Elife. 2015 Aug 27;4:e09073. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09073. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26312500 Free PMC article.
-
A dual role for DNA binding by Runt in activation and repression of sloppy paired transcription.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Nov 1;32(21):ar26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-08-0509. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34432496 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence That Runt Acts as a Counter-Repressor of Groucho During Drosophila melanogaster Primary Sex Determination.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Jul 7;10(7):2487-2496. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401384. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32457096 Free PMC article.
-
Direct recruitment of polycomb repressive complex 1 to chromatin by core binding transcription factors.Mol Cell. 2012 Feb 10;45(3):330-43. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.032. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22325351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao R., Friedrich M. Conserved cluster organization of insect Runx genes. Dev. Genes Evol. 2008;218:567–574. - PubMed
-
- Bravo J., Li Z., Speck N. A., Warren A. J. The leukemia-associated AML1 (Runx1)–CBF beta complex functions as a DNA-induced molecular clamp. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001;8:371–378. - PubMed
-
- de Bruijn M. F., Speck N. A. Core-binding factors in hematopoiesis and immune function. Oncogene. 2004;23:4238–4248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

