Protein kinase C isoforms zeta and iota mediate collagenase expression and cartilage destruction via STAT3- and ERK-dependent c-fos induction
- PMID: 20463008
- PMCID: PMC2903406
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.120121
Protein kinase C isoforms zeta and iota mediate collagenase expression and cartilage destruction via STAT3- and ERK-dependent c-fos induction
Abstract
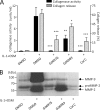
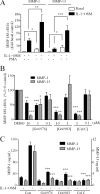
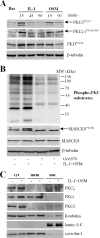
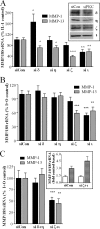
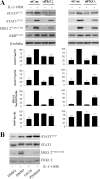
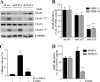
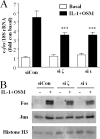
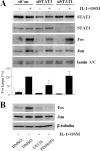
The protein kinase C (PKC) signaling pathway is a major regulator of cellular functions and is implicated in pathologies involving extracellular matrix remodeling. Inflammatory joint disease is characterized by excessive extracellular matrix catabolism, and here we assess the role of PKC in the induction of the collagenases, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and MMP-13, in human chondrocytes by the potent cytokine stimulus interleukin-1 (IL-1) in combination with oncostatin M (OSM). IL-1 + OSM-stimulated collagenolysis and gelatinase activity were ameliorated by pharmacological PKC inhibition in bovine cartilage, as was collagenase gene induction in human chondrocytes. Small interfering RNA-mediated silencing of PKC gene expression showed that both novel (nPKC delta, nPKC eta) and atypical (aPKC zeta, aPKC iota) isoforms were involved in collagenase induction by IL-1. However, MMP1 and MMP13 induction by IL-1 + OSM was inhibited only by aPKC silencing, suggesting that only atypical isoforms play a significant role in complex inflammatory milieus. Silencing of either aPKC led to diminished IL-1 + OSM-dependent extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 phosphorylation, and c-fos expression. STAT3 gene silencing or ERK pathway inhibition also resulted in loss of IL-1 + OSM-stimulated c-fos and collagenase expression. Silencing of c-fos and c-jun expression was sufficient to abrogate IL-1 + OSM-stimulated collagenase gene induction, and overexpression of both c-fos and c-jun was sufficient to drive transcription from the MMP1 promoter in the absence of a stimulus. Our data identify atypical PKC isozymes as STAT and ERK activators that mediate c-fos and collagenase expression during IL-1 + OSM synergy in human chondrocytes. aPKCs may constitute potential therapeutic targets for inflammatory joint diseases involving increased collagenase expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic collagenase expression and cartilage collagenolysis are phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling-dependent.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 23;283(21):14221-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710136200. Epub 2008 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18332138
-
Protein kinase D3 modulates MMP1 and MMP13 expression in human chondrocytes.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 13;13(4):e0195864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195864. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29652915 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways implicated in oncostatin M-induced aggrecanase-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in human articular chondrocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Mar;1773(3):309-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.11.018. Epub 2006 Dec 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17208315
-
Oncostatin M-induced matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 genes expression in chondrocytes requires Janus kinase/STAT signaling pathway.J Immunol. 2001 Mar 1;166(5):3491-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.5.3491. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11207308
-
Atypical protein kinase Cι as a human oncogene and therapeutic target.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Mar 1;88(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.10.023. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24231509 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Function of the chondrocyte PI-3 kinase-Akt signaling pathway is stimulus dependent.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015 Jun;23(6):949-56. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2015.01.014. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015. PMID: 25659655 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the Par3 polarity protein promotes breast tumorigenesis and metastasis.Cancer Cell. 2012 Nov 13;22(5):601-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.10.003. Cancer Cell. 2012. PMID: 23153534 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of a chloracne phenotype in an epidermal equivalent model by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) is dependent on aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation and is not reproduced by aryl hydrocarbon receptor knock down.J Dermatol Sci. 2014 Jan;73(1):10-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Dermatol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24161567 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism: signals and multiple effectors converge upon MMP-13 regulation in osteoarthritis.Eur Cell Mater. 2011 Feb 24;21:202-20. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v021a16. Eur Cell Mater. 2011. PMID: 21351054 Free PMC article.
-
The Proto-oncogene PKCι regulates the alternative splicing of Bcl-x pre-mRNA.Mol Cancer Res. 2012 May;10(5):660-9. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0363. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Mol Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22522453 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

