Opposing effects of a tyrosine-based sorting motif and a PDZ-binding motif regulate human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 envelope trafficking
- PMID: 20463077
- PMCID: PMC2898256
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01853-09
Opposing effects of a tyrosine-based sorting motif and a PDZ-binding motif regulate human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 envelope trafficking
Abstract
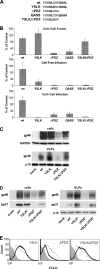
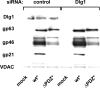
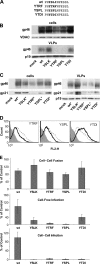
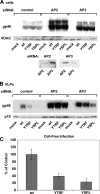
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) envelope (Env) glycoprotein mediates binding of the virus to its receptor on the surface of target cells and subsequent fusion of virus and cell membranes. To better understand the mechanisms that control HTLV-1 Env trafficking and activity, we have examined two protein-protein interaction motifs in the cytoplasmic domain of Env. One is the sequence YSLI, which matches the consensus YXXPhi motifs that are known to interact with various adaptor protein complexes; the other is the sequence ESSL at the C terminus of Env, which matches the consensus PDZ-binding motif. We show here that mutations that destroy the YXXPhi motif increased Env expression on the cell surface and increased cell-cell fusion activity. In contrast, mutation of the PDZ-binding motif greatly diminished Env expression in cells, which could be restored to wild-type levels either by mutating the YXXPhi motif or by silencing AP2 and AP3, suggesting that interactions with PDZ proteins oppose an Env degradation pathway mediated by AP2 and AP3. Silencing of the PDZ protein hDlg1 did not affect Env expression, suggesting that hDlg1 is not a binding partner for Env. Substitution of the YSLI sequence in HTLV-1 Env with YXXPhi elements from other cell or virus membrane-spanning proteins resulted in alterations in Env accumulation in cells, incorporation into virions, and virion infectivity. Env variants containing YXXPhi motifs that are predicted to have high-affinity interaction with AP2 accumulated to lower steady-state levels. Interestingly, mutations that destroy the YXXPhi motif resulted in viruses that were not infectious by cell-free or cell-associated routes of infection. Unlike YXXPhi, the function of the PDZ-binding motif manifests itself only in the producer cells; AP2 silencing restored the incorporation of PDZ-deficient Env into virus-like particles (VLPs) and the infectivity of these VLPs to wild-type levels.
Figures


References
-
- Berlioz-Torrent, C., B. L. Shacklett, L. Erdtmann, L. Delamarre, I. Bouchaert, P. Sonigo, M. C. Dokhelar, and R. Benarous. 1999. Interactions of the cytoplasmic domains of human and simian retroviral transmembrane proteins with components of the clathrin adaptor complexes modulate intracellular and cell surface expression of envelope glycoproteins. J. Virol. 73:1350-1361. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blot, V., L. Delamarre, F. Perugi, D. Pham, S. Benichou, R. Benarous, T. Hanada, A. H. Chishti, M. C. Dokhelar, and C. Pique. 2004. Human Dlg protein binds to the envelope glycoproteins of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 and regulates envelope mediated cell-cell fusion in T lymphocytes. J. Cell Sci. 117:3983-3993. - PubMed
-
- Bobkova, M., J. Stitz, M. Engelstadter, K. Cichutek, and C. J. Buchholz. 2002. Identification of R-peptides in envelope proteins of C-type retroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 83:2241-2246. - PubMed
-
- Boge, M., S. Wyss, J. S. Bonifacino, and M. Thali. 1998. A membrane-proximal tyrosine-based signal mediates internalization of the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein via interaction with the AP-2 clathrin adaptor. J. Biol. Chem. 273:15773-15778. - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino, J. S., and L. M. Traub. 2003. Signals for sorting of transmembrane proteins to endosomes and lysosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72:395-447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

