OrfA downregulates feline immunodeficiency virus primary receptor CD134 on the host cell surface and is important in viral infection
- PMID: 20463078
- PMCID: PMC2898258
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00434-10
OrfA downregulates feline immunodeficiency virus primary receptor CD134 on the host cell surface and is important in viral infection
Abstract
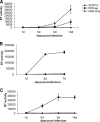
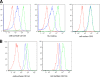
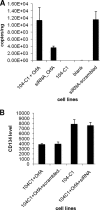
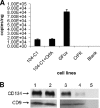
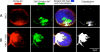
Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) OrfA is an accessory protein that is critical for productive viral replication and infection in T cells. Here, we show that OrfA acts to markedly reduce cell surface expression of the FIV primary binding receptor. Downregulation does not occur at the transcriptional or translational level in that the amounts of CD134 mRNA and protein in total cell lysates are not altered between parental 104-C1 T cells and the same cell line stably expressing OrfA (104-C1-OrfA). Analysis by confocal microscopy revealed significant accumulation of CD134 in the Golgi apparatus of 104-C1 cells expressing OrfA. OrfA does not cause a generalized disruption of membrane trafficking in that surface expression of CD9 is unaffected by OrfA overexpression. Consistent with the above observations, OrfA-negative FIV-34TF10 productively infects CrFK (CD134-negative) and 104-C1-OrfA (CD134 downregulated by OrfA) cells but fails to productively infect either 104-C1 (CD134-positive) cells or GFox (CrFK cells overexpressing CD134) cells. FIV-34TF10 in which the OrfA reading frame is open (OrfArep) productively infects CrFK, GFox, 104-C1, and 104-C1-OrfA cells. We hypothesize that reduced surface expression of the receptor, a hallmark of retrovirus infections, may facilitate an increase in virus release from the infected cell by minimizing receptor interactions with budding virus particles.
Figures
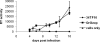
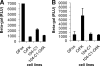
References
-
- de Parseval, A., U. Chatterji, G. Morris, P. Sun, A. J. Olson, and J. H. Elder. 2005. Structural mapping of CD134 residues critical for interaction with feline immunodeficiency virus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12:60-66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

