Sodium/calcium exchangers selectively regulate calcium signaling in mouse taste receptor cells
- PMID: 20463203
- PMCID: PMC2904227
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00118.2010
Sodium/calcium exchangers selectively regulate calcium signaling in mouse taste receptor cells
Abstract
Taste cells use multiple signaling mechanisms to generate appropriate cellular responses to discrete taste stimuli. Some taste stimuli activate G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) that cause calcium release from intracellular stores while other stimuli depolarize taste cells to cause calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). While the signaling mechanisms that initiate calcium signals have been described in taste cells, the calcium clearance mechanisms (CCMs) that contribute to the termination of these signals have not been identified. In this study, we used calcium imaging to define the role of sodium-calcium exchangers (NCXs) in the termination of evoked calcium responses. We found that NCXs regulate the calcium signals that rely on calcium influx at the plasma membrane but do not significantly contribute to the calcium signals that depend on calcium release from internal stores. Our data indicate that this selective regulation of calcium signals by NCXs is due primarily to their location in the cell rather than to the differences in cytosolic calcium loads. This is the first report to define the physiological role for any of the CCMs utilized by taste cells to regulate their evoked calcium responses.
Figures

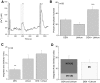
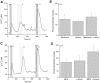

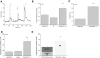
References
-
- Akabas MH, Dodd J, Al-Awqati Q. A bitter substance induces a rise in intracellular calcium in a subpopulation of rat taste cells. Science 242: 1047–1050, 1988 - PubMed
-
- Augustine GJ, Santamaria F, Tanaka K. Local calcium signaling in neurons. Neuron 40: 331–346, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Lipp P. Calcium—a life and death signal. Nature 395: 645–648, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Blaustein MP. Calcium transport and buffering in neurons. Trends Neurosci 11: 438–443, 1988 - PubMed
-
- Blaustein MP, Juhaszova M, Golovina VA, Church PJ, Stanley EF. Na/Ca exchanger and PMCA localization in neurons and astrocytes: functional implications. Ann NY Acad Sci 976: 356–366, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

