Tissue plasminogen activator alters intracellular sequestration of zinc through interaction with the transporter ZIP4
- PMID: 20463217
- PMCID: PMC2872103
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6250-09.2010
Tissue plasminogen activator alters intracellular sequestration of zinc through interaction with the transporter ZIP4
Abstract
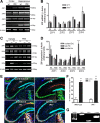
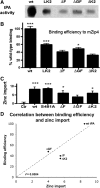
Glutamatergic neurons contain free zinc packaged into neurotransmitter-loaded synaptic vesicles. Upon neuronal activation, the vesicular contents are released into the synaptic space, whereby the zinc modulates activity of postsynaptic neurons though interactions with receptors, transporters and exchangers. However, high extracellular concentrations of zinc trigger seizures and are neurotoxic if substantial amounts of zinc reenter the cells via ion channels and accumulate in the cytoplasm. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), a secreted serine protease, is also proepileptic and excitotoxic. However, tPA counters zinc toxicity by promoting zinc import back into the neurons in a sequestered form that is nontoxic. Here, we identify the zinc influx transporter, ZIP4, as the pathway through which tPA mediates the zinc uptake. We show that ZIP4 is upregulated after excitotoxin stimulation of the mouse, male and female, hippocampus. ZIP4 physically interacts with tPA, correlating with an increased intracellular zinc influx and lysosomal sequestration. Changes in prosurvival signals support the idea that this sequestration results in neuroprotection. These experiments identify a mechanism via which neurons use tPA to efficiently neutralize the toxic effects of excessive concentrations of free zinc.
Figures





References
-
- Andrade-Gordon P, Strickland S. Interaction of heparin with plasminogen activators and plasminogen: effects on the activation of plasminogen. Biochemistry. 1986;25:4033–4040. - PubMed
-
- Choi DW, Koh JY. Zinc and brain injury. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1998;21:347–375. - PubMed
-
- Cornford EM, Nguyen EV, Landaw EM. Acute upregulation of blood-brain barrier glucose transporter activity in seizures. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:H1346–H1354. - PubMed
-
- Coulter D. Mossy fiber zinc and temporal lobe epilepsy: pathological association with altered “epileptic” gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors in dentate granule cells. Epilepsia. 2000;41(Suppl 6):S96–S99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
