Evidence for the involvement of Lfc and Tctex-1 in axon formation
- PMID: 20463241
- PMCID: PMC3845415
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5420-09.2010
Evidence for the involvement of Lfc and Tctex-1 in axon formation
Abstract
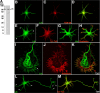
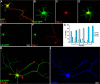
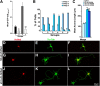
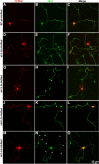
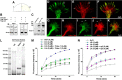
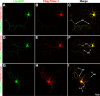
RhoA and Rac play key and opposite roles during neuronal polarization. We now show that Lfc, a guanosine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF), localizes to the Golgi apparatus and growth cones of developing neurons and negatively regulates neurite sprouting and axon formation through a Rho signaling pathway. Tctex-1, a dynein light chain implicated in axon outgrowth by modulating actin dynamics and Rac activity, colocalizes and physically interacts with Lfc, thus inhibiting its GEF activity, decreasing Rho-GTP levels, and functionally antagonizing Lfc during neurite formation.
Figures
References
-
- Aijaz S, D'Atri F, Citi S, Balda MS, Matter K. Binding of GEF-H1 to the tight junction-associated adaptor cingulin results in inhibition of Rho signaling and G1/S phase transition. Dev Cell. 2005;8:777–786. - PubMed
-
- Arimura A, Kaibuchi K. Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:194–205. - PubMed
-
- Bhupinder P, Vohra S, Fu M, Heuckeroth RO. Protein kinase Czeta and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta control neuronal polarity in developing rodent enteric neurons, whereas SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 promotes neurite growth but does not influence polarity. J Neurosci. 2007;27:9458–9468. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birkenfeld J, Nalbant P, Yoon S, Bokoch G. Cellular functions of GEF-H1, a microtubule regulated Rho-GEF: is altered GEF-H1 activity a crucial determinant of disease pathogenesis? Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18:210–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
