Isometric quadriceps strength in women with mild, moderate, and severe knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 20463561
- PMCID: PMC3294452
- DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0b013e3181ddd5c3
Isometric quadriceps strength in women with mild, moderate, and severe knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Objective: Quadriceps weakness is a common clinical sign in persons with moderate-to-severe osteoarthritis and results in physical disability; however, minimal data exist to establish whether quadriceps weakness is present in early stages of the disease. Therefore, our purpose was to determine whether quadriceps weakness was present in persons with early radiographic and cartilaginous evidence of osteoarthritis. Further, we sought to determine whether quadriceps strength decreases as osteoarthritis severity increases.
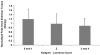
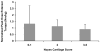
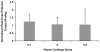
Design: Three hundred forty-eight women completed radiologic and magnetic resonance imaging evaluation, in addition to strength testing. Anterior-posterior radiographs were graded for tibiofemoral osteoarthritis severity using the Kellgren-Lawrence scale. Scans from magnetic resonance imaging were used to assess medial tibiofemoral and patellar cartilage based on a modification of the Noyes scale. The peak knee extension torque recorded was used to represent strength.
Results: Quadriceps strength (Nm/kg) was 22% greater in women without radiographic osteoarthritis than in women with osteoarthritis (P < 0.05). Quadriceps strength was also greater in women with Noyes' medial tibial and femoral cartilage scores of 0 when compared in women with Noyes' grades 2 and 3-5 (P < or = 0.05).
Conclusions: Women with early evidence of osteoarthritis had less quadriceps strength than women without osteoarthritis as defined by imaging.
Figures
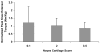
References
-
- Dillon CF, Rasch EK, Gu Q, et al. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the United States: Arthritis data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1991–94. J Rheumatol. 2006;33:2271–9. - PubMed
-
- Hootman JM, Helmick CG. Projections of US prevalence of arthritis and associated activity limitations. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:226–9. - PubMed
-
- Hootman J, Fitzgerald S, Macera C, et al. Lower extremity muscle strength and risk of self-reported hip or knee osteoarthritis. J Phys Act Health. 2004;1:321–30.
-
- Slemenda C, Brandt KD, Heilman DK, et al. Quadriceps weakness and osteoarthritis of the knee. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127:97–104. - PubMed
-
- Messier SP, Loeser RG, Hoover JL, et al. Osteoarthritis of the knee: Effects on gait, strength, and flexibility. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1992;73:29–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AG012553/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG017104/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012554/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012539/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012531/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NR004061/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012554/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012553/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NR004061/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012539/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012495/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017104/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG012531/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG012505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

