Effects of IL-2 on MMP expression in freshly isolated human NK cells and the IL-2-independent NK cell line YT
- PMID: 20463600
- PMCID: PMC2877139
- DOI: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181d372a0
Effects of IL-2 on MMP expression in freshly isolated human NK cells and the IL-2-independent NK cell line YT
Abstract
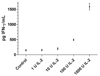
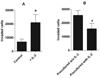
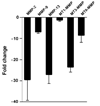
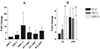
Interleukin-2 is an important activation factor for natural killer (NK) cells but its effect on NK cell matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) production and matrix degradation is less well investigated. We have used freshly isolated human NK cells and the IL-2-independent NK cell line, YT, to investigate the effects of IL-2 stimulation on NK cell invasion of Matrigel and on MMP expression and production. In YT cells, we found opposing early and late effects of IL-2 stimulation with an early (2 h) increase in MMP-9 protein level and enhanced migration in the Matrigel invasion assay and by 30 hours a decreased mRNA expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, MMP-13, MT3-MMP, and MT6-MMP. We also found a preculture period of 48 hours with IL-2 to negatively affect YT cell migration. We furthermore found that freshly isolated human NK cells Matrigel invasion was MMP-dependent and it increased in response to IL-2. Importantly, in freshly isolated human NK cells we did not see a downregulation of MMPs after 24 hours IL-2 stimulation, but instead a significant upregulation of MT6-MMP mRNA. Because of the cellular localisation of MT6-MMP, which ensures a focalized proteolytic activity, and its high expression compared with the other MMPs in freshly isolated human NK cells makes it of interest to study further.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human NK cell lines migrate differentially in vitro related to matrix interaction and MMP expression.Immunol Cell Biol. 2009 Aug-Sep;87(6):489-95. doi: 10.1038/icb.2009.35. Epub 2009 May 12. Immunol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19434071
-
Membrane-type 6 matrix metalloproteinase regulates the activation-induced downmodulation of CD16 in human primary NK cells.J Immunol. 2013 Aug 15;191(4):1883-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300313. Epub 2013 Jul 12. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23851692 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted and membrane-associated matrix metalloproteinases of IL-2-activated NK cells and their inhibitors.J Immunol. 2000 Jun 1;164(11):5883-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.11.5883. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10820269
-
Matrix metalloproteinases of human NK cells.In Vivo. 2000 Jan-Feb;14(1):269-76. In Vivo. 2000. PMID: 10757086
-
The role of IL-18 in the modulation of matrix metalloproteinases and migration of human natural killer (NK) cells.FEBS Lett. 2004 Jul 2;569(1-3):156-60. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.05.039. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15225625
Cited by
-
Stem cells-derived natural killer cells for cancer immunotherapy: current protocols, feasibility, and benefits of ex vivo generated natural killer cells in treatment of advanced solid tumors.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Dec;70(12):3369-3395. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02975-8. Epub 2021 Jul 4. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 34218295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biology of NK cells and their receptors affects clinical outcomes after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT).Immunol Rev. 2014 Mar;258(1):45-63. doi: 10.1111/imr.12157. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24517425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Killer Cell Adoptive Transfer Therapy: Exploiting the First Line of Defense Against Cancer.Cancer J. 2015 Nov-Dec;21(6):486-91. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000156. Cancer J. 2015. PMID: 26588681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Immune-Related Genes Concurrently Involved in Critical Illnesses Across Different Etiologies: A Data-Driven Analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 9;13:858864. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.858864. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35615364 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases in cytotoxic lymphocytes impact on tumour infiltration and immunomodulation.Cancer Microenviron. 2011 Dec;4(3):351-60. doi: 10.1007/s12307-010-0057-0. Epub 2010 Nov 27. Cancer Microenviron. 2011. PMID: 22161319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertsson PA, Basse PH, Hokland M, et al. NK cells and the tumour microenvironment: implications for NK-cell function and anti-tumour activity. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:603–609. - PubMed
-
- Hagenaars M, Ensink NG, Basse PH, et al. The microscopic anatomy of experimental rat CC531 colon tumour metastases: consequences for immunotherapy? Clin Exp Metastasis. 2000;18:189–196. - PubMed
-
- Kuppen PJ, van der Eb MM, Jonges LE, et al. Tumor structure and extracellular matrix as a possible barrier for therapeutic approaches using immune cells or adenoviruses in colorectal cancer. Histochem Cell Biol. 2001;115:67–72. - PubMed
-
- Yang Q, Hokland ME, Bryant JL, et al. Tumor-localization by adoptively transferred, interleukin-2-activated NK cells leads to destruction of well-established lung metastases. Int J Cancer. 2003;105:512–519. - PubMed
-
- Kim MH, Kitson RP, Albertsson P, et al. Secreted and membrane-associated matrix metalloproteinases of IL-2-activated NK cells and their inhibitors. J Immunol. 2000;164:5883–5889. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

