Penalized model-based clustering with unconstrained covariance matrices
- PMID: 20463857
- PMCID: PMC2867492
- DOI: 10.1214/09-EJS487
Penalized model-based clustering with unconstrained covariance matrices
Abstract
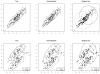
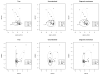
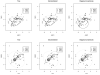
Clustering is one of the most useful tools for high-dimensional analysis, e.g., for microarray data. It becomes challenging in presence of a large number of noise variables, which may mask underlying clustering structures. Therefore, noise removal through variable selection is necessary. One effective way is regularization for simultaneous parameter estimation and variable selection in model-based clustering. However, existing methods focus on regularizing the mean parameters representing centers of clusters, ignoring dependencies among variables within clusters, leading to incorrect orientations or shapes of the resulting clusters. In this article, we propose a regularized Gaussian mixture model permitting a treatment of general covariance matrices, taking various dependencies into account. At the same time, this approach shrinks the means and covariance matrices, achieving better clustering and variable selection. To overcome one technical challenge in estimating possibly large covariance matrices, we derive an E-M algorithm utilizing the graphical lasso (Friedman et al 2007) for parameter estimation. Numerical examples, including applications to microarray gene expression data, demonstrate the utility of the proposed method.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Penalized model-based clustering with cluster-specific diagonal covariance matrices and grouped variables.Electron J Stat. 2008;2:168-212. doi: 10.1214/08-EJS194. Electron J Stat. 2008. PMID: 19920875 Free PMC article.
-
Penalized mixtures of factor analyzers with application to clustering high-dimensional microarray data.Bioinformatics. 2010 Feb 15;26(4):501-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp707. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20031967 Free PMC article.
-
Regularized Gaussian Mixture Model for High-Dimensional Clustering.IEEE Trans Cybern. 2019 Oct;49(10):3677-3688. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2846404. Epub 2018 Jun 27. IEEE Trans Cybern. 2019. PMID: 29994696
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Model-based approaches to synthesize microarray data: a unifying review using mixture of SEMs.Stat Methods Med Res. 2013 Dec;22(6):567-82. doi: 10.1177/0962280211419482. Epub 2011 Sep 25. Stat Methods Med Res. 2013. PMID: 21948997 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous clustering and estimation of networks in multiple graphical models.Biostatistics. 2024 Dec 31;26(1):kxae015. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxae015. Biostatistics. 2024. PMID: 38841872 Free PMC article.
-
Graph-based sparse linear discriminant analysis for high-dimensional classification.J Multivar Anal. 2019 May;171:250-269. doi: 10.1016/j.jmva.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Multivar Anal. 2019. PMID: 31983784 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer subtype discovery and biomarker identification via a new robust network clustering algorithm.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 17;8(6):e66256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066256. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23799085 Free PMC article.
-
OUTCOME-GUIDED DISEASE SUBTYPING BY GENERATIVE MODEL AND WEIGHTED JOINT LIKELIHOOD IN TRANSCRIPTOMIC APPLICATIONS.Ann Appl Stat. 2024 Sep;18(3):1947-1964. doi: 10.1214/23-aoas1865. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Ann Appl Stat. 2024. PMID: 40740430 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular heterogeneity at the network level: high-dimensional testing, clustering and a TCGA case study.Bioinformatics. 2017 Sep 15;33(18):2890-2896. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx322. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28535188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alaiya AA, et al. Molecular classification of borderline ovarian tumors using hierarchical cluster analysis of protein expression profiles. Int. J. Cancer. 2002;98:895–899. - PubMed
-
- Banfield JD, Raftery AE. Model-Based Gaussian and Non-Gaussian Clustering. Biometrics. 1993;49:803–821.
-
- Bardi E, Bobok I, Olah AV, Olah E, Kappelmayer J, Kiss C. Cystatin C is a suitable marker of glomerular function in children with cancer. Pediatric Nephrology. 2004;19:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho CM, Scott JG. Objective Bayesian model selection in Gaussian graphical models. Biometrika. 2009;96:497–512.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
