Myeloid cell-restricted insulin receptor deficiency protects against obesity-induced inflammation and systemic insulin resistance
- PMID: 20463885
- PMCID: PMC2865520
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000938
Myeloid cell-restricted insulin receptor deficiency protects against obesity-induced inflammation and systemic insulin resistance
Abstract
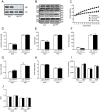
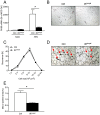
A major component of obesity-related insulin resistance is the establishment of a chronic inflammatory state with invasion of white adipose tissue by mononuclear cells. This results in the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn leads to insulin resistance in target tissues such as skeletal muscle and liver. To determine the role of insulin action in macrophages and monocytes in obesity-associated insulin resistance, we conditionally inactivated the insulin receptor (IR) gene in myeloid lineage cells in mice (IR(Deltamyel)-mice). While these animals exhibit unaltered glucose metabolism on a normal diet, they are protected from the development of obesity-associated insulin resistance upon high fat feeding. Euglycemic, hyperinsulinemic clamp studies demonstrate that this results from decreased basal hepatic glucose production and from increased insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in skeletal muscle. Furthermore, IR(Deltamyel)-mice exhibit decreased concentrations of circulating tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha and thus reduced c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activity in skeletal muscle upon high fat feeding, reflecting a dramatic reduction of the chronic and systemic low-grade inflammatory state associated with obesity. This is paralleled by a reduced accumulation of macrophages in white adipose tissue due to a pronounced impairment of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 9 expression and activity in these cells. These data indicate that insulin action in myeloid cells plays an unexpected, critical role in the regulation of macrophage invasion into white adipose tissue and in the development of obesity-associated insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
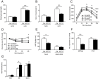
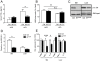

References
-
- Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993;259:87–91. - PubMed
-
- Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L, Ranganathan G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;280:E745–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

