Atomic force microscopy probing in the measurement of cell mechanics
- PMID: 20463929
- PMCID: PMC2865008
- DOI: 10.2147/ijn.s5787
Atomic force microscopy probing in the measurement of cell mechanics
Abstract
Atomic force microscope (AFM) has been used incrementally over the last decade in cell biology. Beyond its usefulness in high resolution imaging, AFM also has unique capabilities for probing the viscoelastic properties of living cells in culture and, even more, mapping the spatial distribution of cell mechanical properties, providing thus an indirect indicator of the structure and function of the underlying cytoskeleton and cell organelles. AFM measurements have boosted our understanding of cell mechanics in normal and diseased states and provide future potential in the study of disease pathophysiology and in the establishment of novel diagnostic and treatment options.
Keywords: atomic force microscopy; cell elastography; cell force spectroscopy; cell mechanics.
Figures
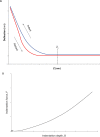
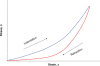
Similar articles
-
Single-cell elastography: probing for disease with the atomic force microscope.Dis Markers. 2003-2004;19(2-3):139-54. doi: 10.1155/2004/482680. Dis Markers. 2003. PMID: 15096710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of atomic force microscopy measurements on cardiovascular cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;843:229-44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-523-7_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22222537
-
Atomic Force Microscopy in Characterizing Cell Mechanics for Biomedical Applications: A Review.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2017 Sep;16(6):523-540. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2017.2714462. Epub 2017 Jun 9. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2017. PMID: 28613180 Review.
-
In situ sensing and manipulation of molecules in biological samples using a nanorobotic system.Nanomedicine. 2005 Mar;1(1):31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2004.11.005. Nanomedicine. 2005. PMID: 17292055
-
Atomic force microscopy probing of cell elasticity.Micron. 2007;38(8):824-33. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2007.06.011. Epub 2007 Jul 3. Micron. 2007. PMID: 17709250
Cited by
-
Microfluidics-based assessment of cell deformability.Anal Chem. 2012 Aug 7;84(15):6438-43. doi: 10.1021/ac300264v. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22746217 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of cytoplasmic viscosity of hundreds of single tumour cells based on micropipette aspiration.R Soc Open Sci. 2019 Mar 20;6(3):181707. doi: 10.1098/rsos.181707. eCollection 2019 Mar. R Soc Open Sci. 2019. PMID: 31032026 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the elastic properties of tissues.Mater Today (Kidlington). 2011 Mar;14(3):96-105. doi: 10.1016/S1369-7021(11)70059-1. Mater Today (Kidlington). 2011. PMID: 22723736 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically encoded force sensors for measuring mechanical forces in proteins.Commun Integr Biol. 2011 Jul;4(4):385-90. doi: 10.4161/cib.15505. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Commun Integr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21966553 Free PMC article.
-
Atomic force microscopy study of the arrangement and mechanical properties of astrocytic cytoskeleton in growth medium.Acta Naturae. 2011 Jul;3(3):93-9. Acta Naturae. 2011. PMID: 22649699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhu C, Bao G, Wang N. Cell mechanics: mechanical response, cell adhesion, and molecular deformation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2000;2:189–226. - PubMed
-
- Elson EL. Cellular mechanics as an indicator of cytoskeletal structure and function. Annu Rev Biophys Chem. 1988;17:397–430. - PubMed
-
- Pourati J, Maniotis A, Spiegel D, et al. Is cytoskeletal tension a major determinant of cell deformability in adherent endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1998;247:C1283–C1289. - PubMed
-
- Trickey WR, Vail TP, Guilak F. The role of the cytoskeleton in the viscoelastic properties of human articular chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2004;22:131–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

