p53-induced growth arrest is regulated by the mitochondrial SirT3 deacetylase
- PMID: 20463968
- PMCID: PMC2864751
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010486
p53-induced growth arrest is regulated by the mitochondrial SirT3 deacetylase
Abstract
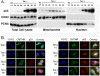
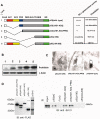
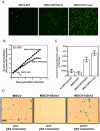
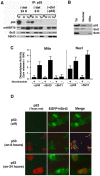
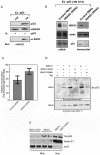
A hallmark of p53 function is to regulate a transcriptional program in response to extracellular and intracellular stress that directs cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and cellular senescence. Independent of the role of p53 in the nucleus, some of the anti-proliferative functions of p53 reside within the mitochondria [1]. p53 can arrest cell growth in response to mitochondrial p53 in an EJ bladder carcinoma cell environment that is naïve of p53 function until induced to express p53 [2]. TP53 can independently partition with endogenous nuclear and mitochondrial proteins consistent with the ability of p53 to enact senescence. In order to address the role of p53 in navigating cellular senescence through the mitochondria, we identified SirT3 to rescue EJ/p53 cells from induced p53-mediated growth arrest. Human SirT3 function appears coupled with p53 early during the initiation of p53 expression in the mitochondria by biochemical and cellular localization analysis. Our evidence suggests that SirT3 partially abrogates p53 activity to enact growth arrest and senescence. Additionally, we identified the chaperone protein BAG-2 in averting SirT3 targeting of p53 -mediated senescence. These studies identify a complex relationship between p53, SirT3, and chaperoning factor BAG-2 that may link the salvaging and quality assurance of the p53 protein for control of cellular fate independent of transcriptional activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
SirT3 and p53 Deacetylation in Aging and Cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Sep;232(9):2308-2311. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25669. Epub 2017 Apr 10. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27791271 Review.
-
Minnelide/Triptolide Impairs Mitochondrial Function by Regulating SIRT3 in P53-Dependent Manner in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 8;11(8):e0160783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160783. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27501149 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 3 induces apoptosis and necroptosis by regulating mutant p53 expression in small‑cell lung cancer.Oncol Rep. 2020 Feb;43(2):591-600. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7439. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 31894331
-
SIRT3 protects endothelial cells from high glucose-induced senescence and dysfunction via the p53 pathway.Life Sci. 2021 Jan 1;264:118724. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118724. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33160987
-
Sirtuin-3 (SIRT3), a therapeutic target with oncogenic and tumor-suppressive function in cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Feb 6;5(2):e1047. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.14. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24503539 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Artificial Reaction Promoter Modulates Mitochondrial Functions via Chemically Promoting Protein Acetylation.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 4;6:29224. doi: 10.1038/srep29224. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27374857 Free PMC article.
-
Expression/localization patterns of sirtuins (SIRT1, SIRT2, and SIRT7) during progression of cervical cancer and effects of sirtuin inhibitors on growth of cervical cancer cells.Tumour Biol. 2015 Aug;36(8):6159-71. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3300-y. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25794641
-
Role of BAG5 in Protein Quality Control: Double-Edged Sword?Front Aging. 2022 Mar 3;3:844168. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.844168. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 35821856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuins: guardians of mammalian healthspan.Trends Genet. 2014 Jul;30(7):271-86. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.04.007. Epub 2014 May 28. Trends Genet. 2014. PMID: 24877878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT3 is a novel prognostic biomarker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Med Oncol. 2014 Aug;31(8):103. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0103-8. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25005846
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

