Characterization of the Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) binding pocket: NMR-based screening identifies small-molecule ligands
- PMID: 20463977
- PMCID: PMC2864760
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010479
Characterization of the Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP) binding pocket: NMR-based screening identifies small-molecule ligands
Abstract
Background: Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP), also known as phoshaptidylethanolamine binding protein (PEBP), has been shown to inhibit Raf and thereby negatively regulate growth factor signaling by the Raf/MAP kinase pathway. RKIP has also been shown to suppress metastasis. We have previously demonstrated that RKIP/Raf interaction is regulated by two mechanisms: phosphorylation of RKIP at Ser-153, and occupation of RKIP's conserved ligand binding domain with a phospholipid (2-dihexanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; DHPE). In addition to phospholipids, other ligands have been reported to bind this domain; however their binding properties remain uncharacterized.
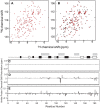
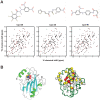
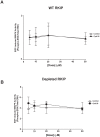
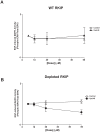
Methods/findings: In this study, we used high-resolution heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy to screen a chemical library and assay a number of potential RKIP ligands for binding to the protein. Surprisingly, many compounds previously postulated as RKIP ligands showed no detectable binding in near-physiological solution conditions even at millimolar concentrations. In contrast, we found three novel ligands for RKIP that specifically bind to the RKIP pocket. Interestingly, unlike the phospholipid, DHPE, these newly identified ligands did not affect RKIP binding to Raf-1 or RKIP phosphorylation. One out of the three ligands displayed off target biological effects, impairing EGF-induced MAPK and metabolic activity.
Conclusions/significance: This work defines the binding properties of RKIP ligands under near physiological conditions, establishing RKIP's affinity for hydrophobic ligands and the importance of bulky aliphatic chains for inhibiting its function. The common structural elements of these compounds defines a minimal requirement for RKIP binding and thus they can be used as lead compounds for future design of RKIP ligands with therapeutic potential.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Trakul N, Menard RE, Schade GR, Qian Z, Rosner MR. Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein Regulates Raf-1 but Not B-Raf Kinase Activation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:24931–24940. - PubMed
-
- Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P, McFerran B, et al. Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature. 1999;401:173–177. - PubMed
-
- Corbit KC, Trakul N, Eves EM, Diaz B, Marshall M, et al. Activation of Raf-1 Signaling by Protein Kinase C through a Mechanism Involving Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13061–13068. - PubMed
-
- Lorenz K, Lohse MJ, Quitterer U. Protein kinase C switches the Raf kinase inhibitor from Raf-1 to GRK-2. Nature. 2003;426:574–579. - PubMed
-
- Keller ET, Fu Z, Yeung K, Brennan M. Raf kinase inhibitor protein: a prostate cancer metastasis suppressor gene. Cancer Lett. 2004;207:131–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

