Antibiotic therapy for prophylaxis against infection of pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 20464721
- PMCID: PMC7138080
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002941.pub3
Antibiotic therapy for prophylaxis against infection of pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic necrosis may complicate severe acute pancreatitis, and is detectable by computed tomography (CT). If it becomes infected mortality increases, but the use of prophylactic antibiotics raises concerns about antibiotic resistance and fungal infection.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy and safety of prophylactic antibiotics in acute pancreatitis complicated by CT proven pancreatic necrosis.
Search strategy: Searches were updated in November 2008, in The Cochrane Library (Issue 2, 2008), MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CINAHL. Conference proceedings and references from found articles were also searched.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing antibiotics versus placebo in acute pancreatitis with CT proven necrosis.
Data collection and analysis: Primary outcomes were mortality and pancreatic infection rates. Secondary end-points included non pancreatic infection, all sites infection, operative rates, fungal infections, and antibiotic resistance. Subgroup analyses were performed for antibiotic regimen (beta-lactam, quinolone, and imipenem).
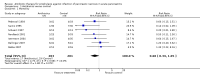
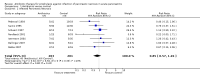
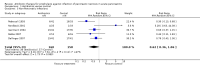
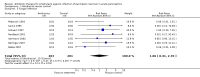
Main results: Seven evaluable studies randomised 404 patients. There was no statistically significant effect on reduction of mortality with therapy: 8.4% versus controls 14.4%, and infected pancreatic necrosis rates: 19.7% versus controls 24.4%. Non-pancreatic infection rates and the incidence of overall infections were not significantly reduced with antibiotics: 23.7% versus 36%; 37.5% versus 51.9% respectively. Operative treatment and fungal infections were not significantly different. Insufficient data were provided concerning antibiotic resistance.With beta-lactam antibiotic prophylaxis there was less mortality (9.4% treatment, 15% controls), and less infected pancreatic necrosis (16.8% treatment group, 24.2% controls) but this was not statistically significant. The incidence of non-pancreatic infections was non-significantly different (21% versus 32.5%), as was the incidence of overall infections (34.4% versus 52.8%), and operative treatment rates. No significant differences were seen with quinolone plus imidazole in any of the end points measured. Imipenem on its own showed no difference in the incidence of mortality, but there was a significant reduction in the rate of pancreatic infection (p=0.02; RR 0.34, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.84).
Authors' conclusions: No benefit of antibiotics in preventing infection of pancreatic necrosis or mortality was found, except for when imipenem (a beta-lactam) was considered on its own, where a significantly decrease in pancreatic infection was found. None of the studies included in this review were adequately powered. Further better designed studies are needed if the use of antibiotic prophylaxis is to be recommended.
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Claudio Bassi was a co‐author of one of the RCTs reviewed (Pederzoli 1993), but did not participate in the meta‐analysis, discussion or conclusions. Professor Mike Larvin and Dr Eduardo Villatoro participated in the later stages of the international multi‐centre study on the role of meropenem for prophylaxis against infection in pancreatic necrosis (Dellinger 2007). The study was sponsored by Astra‐Zeneca who covered local administrative costs, and attendance for both at a mid‐study conference during 2004. Neither investigator has received personal remuneration, nor were they involved as members of the study planning, analysis, or writing committees.
Figures




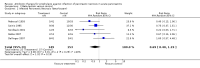
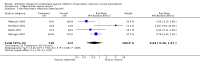
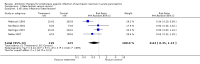











Update of
-
Antibiotic therapy for prophylaxis against infection of pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Oct 18;(4):CD002941. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002941.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 May 12;(5):CD002941. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002941.pub3. PMID: 17054156 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Dellinger 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dellinger EP, Tellado JM, Soto NE, Ashley SW, Barie PS, Dugernier T, Imrie CW, Johnson CD, Knaebel HP, Laterre PF, Maravi‐Poma E, Olsina‐Kissler JJ, Sanchez‐Garcia M, Utzolino S. Early antibiotic treatment for severe Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Annals of Surgery 2007;245(5):674‐83. - PMC - PubMed
Isenmann 2004 {published data only}
-
- Isenmann R, Rünzi M, Kron M, Kahl S, Kraus D, Jung N, Maier L, Malfertheiner P, Goebell H, Beger HG. Prophylactic antibiotic treatment in patients with predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a placebo‐controlled, double‐blind trial. Gastroenterology 2004;126:997‐1004. - PubMed
Nordback 2001 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Nordback I, Sand J, Rauni S, Paajanen H. Early treatment with antibiotics reduces the need for surgery in acute necrotizing pancreatitis ‐ A single‐center randomized study. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2001;5:113‐120. - PubMed
Pederzoli 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pederzoli P, Bassi C, Vesentini S, Campedelli A. A randomized multicenter clinical trial of antibiotic prophylaxis of septic complications in acute necrotizing pancreatitis with imipenem. Surgery, Gynecology & Obstetrics 1993;176:480‐3. - PubMed
Røkke 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Røkke O, Harbitz TB, Liljedal J, Pettersen T, Fetvedt T, Heen LO, Skreden K, Viste A. Early treatment of severe pancreatitis with imipenem: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2007;42:771‐6. - PubMed
Sainio 1995 {published data only}
-
- Sainio V, Kemppainen E, Puolakkainen P, Taavitsainen M, Kivisaari L, Valtonen V, Haapiainen R, Schröder T. Early antibiotic treatment in acute necrotising pancreatitis. The Lancet 1995;346:663‐7. - PubMed
Schwarz 1997 {published data only}
-
- Schwarz M, Isenmann R, Meyer H, Beger HG. Antibiotics in necrotizing pancreatitis. Results of a controlled study. [Antibiotika bei nekrotisierender Pankreatitis]. Dtsch med Wschr 1997;122:356‐61. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Bassi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bassi C, Falconi M, Talamini G, Uomo G, Papaccio G, Dervenis C, Salvia R, Bertazzoni Minelli E, Pederzoli P. Controlled clinical trial of Pefloxacin versus Imipenem in severe acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 1998;115:1513‐7. - PubMed
Craig 1975 {published data only}
-
- Craig RM, Dordal E, Myles L. The use of ampicillin in acute pancreatitis. Annals of Internal Medicine 1975;83:831‐2. - PubMed
Delcenserie 1996 {published data only}
-
- Delcenserie R, Yzet T, Ducroix JP. Prophylactic antibiotics in treatment of severe acute alcoholic pancreatitis. Pancreas 1996;13(2):198‐201. - PubMed
Finch 1976 {published data only}
Gelfand 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gelfand BR, Burnevich SZ, Gelfand EB, Tsydenzhapov ETs, Bryukhov AN, Brazhnik TB, Saganov VP, Pukhaev DA. Efficacy of pefloxacin (Abactal) in the complex treatment of patients with pancreatonecrosis. Antibiot Khimioter 2001;46(5):24‐7. - PubMed
Howes 1975 {published data only}
-
- Howes R, Zuidema GD, Cameron JL. Evaluation of prophylactic antibiotics in acute pancreatitis. Journal of Surgical Research 1975;18:197‐200. - PubMed
Imaizumi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Imaizumi H, Kida M, Nishimaki H, Okuno J, Kataoka Y, Kida Y, Soma K, Saigenji K. Efficacy of continuous regional arterial infusion of a protease inhibitor and antibiotic for severe acute pancreatitis in patients admitted to an intensive care unit. Pancreas 2004;28:369‐73. - PubMed
Luiten 1995 {published data only}
Manes 2006 {published data only}
-
- Manes G, Uomo I, Menchise A, Rabitti PG, Ferrara EC, Uomo G. Timing of antibiotic prophylaxis in acute pancreatitis: a controlled randomised study with meropenem. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2006;101:1348‐53. - PubMed
Maravi‐Poma 2003 {published data only}
-
- Maravi‐Poma E, Gener J, Alvarez‐Lerma F, Olaechea P, Blanco A, Dominguez‐Muñoz JE. Early antibiotic treatment (prophylaxis) of septic complications in severe acute pancreatitis: a prospective, randomized, multicenter study comparing two regimens with imipenem‐cilastatin. Intensive Care Medicine 2003;29:1974‐80. - PubMed
Takeda 1996 {published data only}
-
- Takeda K, Matsuno S, Sunamura M, Kakugawa Y. Continous regional arterial infusion of protease inhibitor and antibiotics in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. American Journal of Surgery 1996;171:394‐8. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Barreda 2009 {published data only}
-
- Barreda L, Targarona J, Milian W, Portugal J, Sequeiros J, Pando E, Calisto JL. Is the prophylactic antibiotic therapy with imipenem effective for patients with pancreatic necrosis? [¿Es la antibióticoterapia profiláctica con imipenem efectiva en los pacientes con necrosis pancreática?]. Acta Gastroenterológica Latinoamericana March 2009;39(1):24‐9. - PubMed
García‐Barrasa 2009 {published data only}
-
- García‐Barrasa A, Borobia FG, Pallares R, Jorba R, Poves I, Busquets J, Fabregat J. A double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of ciprofloxacin prophylaxis in patients with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg 2009;13:768‐74. - PubMed
Spicak 2002 {published data only}
-
- Spicak J, Hubaczova M, Antos F, Bartova J, Cech P, Kasalicky M, Kostka R, lata J, Leffler J, Zavoral M. Antibiotics in the treatment of acute pancreatitis ‐ findings from a randomized multi‐centre prospective study [(Czeck)]. Ceska a Slovenska Gastroenterologie a Hepatologie 2002;56(5):183‐9.
Spicak 2003 {published data only}
-
- Spicak J, Hejtmankova S, Cech P, Hoskovec D, Kostka R, Leffler J, et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis in Severe acute Pancreatitis: Randomized Multicenter Prospective Trial with Meropenem. Ceska a Slovenska Gastroenterologie a Hepatologie 2003;57(6):228‐232.
Spicak 2004 {published data only}
-
- Spicak J, Hejtmankova S, Cech P, Hoskovec D, Kostka R, Leffler J. Antibiotics prophylaxis in large pancreatic necrosis: multicenter randomized trial with ciprofloxacin and metronidazole or meropenem. Gastroenterology 2004;126 (suppl 2):A‐229. [Abstract S1497]
Xue 2009 {published data only}
-
- Xue P, Deng LH, Zhang ZD, Yang XN, Wan MH, Song B, Xia Q. Effect of antibiotic prophylaxis on acute necrotizing pancreatitis: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2009;24:736‐42. - PubMed
Additional references
Ammori 1999
-
- Ammori BJ, Leeder PC, King RF, Barclay GR, Martin IG, Larvin M, McMahon MJ. Early increase in intestinal permeability in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: correlation with endotoxemia, organ failure, and mortality. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 1999;3(3):252‐62. [PMID: 10481118] - PubMed
Barie 1996
-
- Barie PS. A critical review of antibiotic prophylaxis in severe acute pancreatitis. American Journal of Surgery 1996;172(6A):38S‐43S. - PubMed
Bassi 1994a
-
- Bassi C. Infected pancreatic necrosis. International Journal of Pancreatology 1994;16(1):1‐10. - PubMed
Bassi 1994b
Beger 1986
-
- Beger HG, Bittner R, Block S, Buchler M. Bacterial contamination of pancreatic necrosis: a prospective clinical study. Gastroenterology 1986;91(2):433‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bertazzoni 1996
-
- Bertazzoni Minelli E, Benini A, Muner A, Bassi C, Abbas H, Pederzoli P. Pefloxacin penetration into human necrotic pancreatic tissue. Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy 1996;38:237‐43. - PubMed
Bradley 1989
-
- Bradley EL. Antibiotics in acute pancreatitis. Current status and future directions. American Journal of Surgery 1989;158(5):472‐8. - PubMed
Bradley 1993
-
- Bradley EL. A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis: Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Archives of Surgery 1993;128(5):586‐90. - PubMed
Bradley 1999
-
- Bradley III EL. Necrotizing pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1999;86:147‐8. - PubMed
Brown 2004
-
- Brown A. Prophylactic antibiotic use in severe acute pancreatitis: hemlock, help, or hype?. Gastroenterology 2004;126(4):1195‐8. - PubMed
Burns 1986
-
- Burns GP, Stein TA, Kabnick LS. Blood‐pancreatic juice barrier to antibiotic excretion. The American Journal of Surgery 1986;151:205‐8. - PubMed
Büchler 1992
-
- Büchler M, Malfertheiner P, Friess H, Isenmann R, Vanek E, Grimm H, Schlegel P, Friess T, Beger HG. Human pancreatic tissue concentration of bactericidal antibiotics. Gastroenterology 1992;103(6):1902‐8. - PubMed
Büchler 2000
Connor 2004
-
- Connor S, Alexakis N, Neal T, Raraty M, Ghaneh P, Evans J, Hughes M, Rowlands P, Garvey CJ, Sutton R, Neoptolemos JP. Fungal infection but not type of bacterial infection is associated with a high mortality in primary and secondary infected pancreatic necrosis. Digestive Surgery 2004;21(4):297‐304. [PMID: 15365228] - PubMed
De Vries 2007
-
- Vries AC, Besselink MGH, Buskens E, Ridwan BU, Schipper M, Erpecum KJ, Gooszen HG. Quality, effects size and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials of systemic antibiotic prophylaxis in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2007;7:531‐38. - PubMed
De Waele 2003
-
- Waele J, Vogelaers D, Blot S, Colardyn F. Fungal infections in patients with severe acute pancreatitis and the use of prophylactic therapy. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2003;37:208‐13. - PubMed
De Waele 2004
-
- Waele JJ, Vogelaers D, Hoste E, Blot S, Colardyn F. Emergence of antibiotic resistance in infected pancreatic necrosis. Archives of Surgery 2004;139(12):1371‐5. [PMID: 15611464] - PubMed
Dervenis 1999
-
- Dervenis C, Johnson CD, Bassi C, Bradley E, Imrie CW, McMahon MJ, Modlin I. Diagnosis, objective assessment of severity and management of acute pancreatitis. Santorini Consensus Conference. International Journal of Pancreatology 1999;25(3):195‐210. - PubMed
Eatock 1999
-
- Eatock FC, Brombacher GD, Hood J, Carter CR, Imrie CW. Fungal infection of pancreatic necrosis is associated with increased mortality. British Journal of Surgery. 1999; Vol. 86 Suppl. 1:78.
Farkas 1996
-
- Farkas G, Márton J, Mándi Y, Szederkényi E. Surgical strategy and management of infected pancreatic necrosis. British Journal of Surgery 1996;83:930‐3. - PubMed
Fedorak 1992
-
- Fedorak IJ, Ko TC, Djuricin B, McMahon M, Thompson K, Prinz RA. Secondary pancreatic infections: are they distinct clinical entities?. Surgery 1992;112:824‐31. - PubMed
Fenton‐Lee 1993
-
- Fento‐Lee D, Imrie CW. Pancreatic necrosis: Assessment of outcome related to quality of life and cost of management. British Journal of Surgery 1993;80(12):1499‐1500. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Foitzik 1997
Foxx‐Orenstein 1997
-
- Foxx‐Orenstein A, Orenstein R. Antibiotics and pancreatitis. Gastroenterologist 1997;5(2):157‐64. - PubMed
Garg 2001
-
- Garg PK, Khana S, Bohidar NP, Kapil A, Tandon RK. Incidence, spectrum and antibiotic sensitivity pattern of bacterial infections among patients with acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2001;16:1055‐9. - PubMed
Gloor 2001
-
- Gloor B, Müller CA, Worni M, Stahel PF, Redaelli C, Uhl W, Büchler MW. Pancreatic infection in severe pancreatitis; the role of fungus and multiresistant organisms. Archives of Surgery 2001;136:592‐6. - PubMed
Goldacre 2004
Golub 1998
-
- Golub R, Siddiqi F, Pohl D. Role of antibiotics in acute pancreatitis: A meta‐analysis. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 1998;2(6):496‐503. - PubMed
Gotzinger 2001
-
- Gotzinger P, Wamser P, Barlan M, Sautner T, Jakesz R, Fugger R. Candida infection of local necrosis in severe acute pancreatitis is associated with increased mortality. Shock 2000;14:320‐3. - PubMed
Grewe 1999
-
- Grewe M, Tsiotos GG, Luque De‐Leon E, Sarr MG. Fungal infection in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 1999;188(4):408‐14. - PubMed
Heinrich 2006
Ho 1997
-
- Ho hs, Frey CF. The role of antibiotic prophylaxis in severe acute pancreatitis. Archives of Surgery 1997;132:487‐93. - PubMed
Howard 2002
-
- Howard TJ, Temple MB. Prophylactic antibiotics alter the bacteriology of infected necrosis in severe acute pancreatitis. Journal of the American College of Surgeons 2002;195(6):759‐767. [PMID: 12495307] - PubMed
Isenmann 1994
-
- Isenmann R, Büchler MW. Infection and acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1994;81:1707‐8. - PubMed
Johnson 1996
-
- Johnson CD. Antibiotic prophylaxis in severe acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1996;83(7):883‐4. - PubMed
Johnson 2005
Kramer 1999
-
- Kramer KM, Levy H. Prophylactic antibiotics for severe acute pancreatitis: the beginning of an era. Pharmacotherapy 1999;19(5):592‐602. - PubMed
Larvin 1989
-
- Larvin M, Chalmers AG, Robinson PJ, McMahon MJ. Debridement and closed cavity irrigation for the treatment of pancreatic necrosis. British Journal of Surgery 1989;76(5):465‐71. [PMID 2736358] - PubMed
Larvin 1990
Larvin 2008
-
- Larvin M. Management of infected pancreatic necrosis. Current Gastroenterology Reports April 2008;10(2):107‐14. - PubMed
Luiten 1999
-
- Luiten EJT, Bruining HA. Antimicrobial prophylaxis in acute pancreatitis: selective decontamination versus antibiotics. Ballière's best practice and research 1999;13(2):317‐30. - PubMed
Mazaki 2006
-
- Mazaki T, Ishii Y, Takayama T. Meta‐analysis of prophylactic antibiotic use in acute necrotizing pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 2006;93:674‐84. - PubMed
O'Reilly 2004
Powell 1998
-
- Powell JJ, Miles R, Siriwardena AK. Antibiotic prophylaxis in the initial management of severe acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1998;85:582‐7. - PubMed
Powell 1999
-
- Powell JJ, Campbell E, Johnson CD, Siriwardena AK. Survey of antibiotic prophylaxis in the treatment of acute pancreatitis. British Journal of Surgery 1999;86(3):320‐2. - PubMed
Rahman 2003
-
- Rahman SH, Ammori BJ, Holmfield J, Larvin M, McMahon MJ. Intestinal hypoperfusion contributes to gut barrier failure in severe acute pancreatitis. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 2003;7(1):26‐35. [PMID: 12559182] - PubMed
Ratschko 1999
-
- Ratschko M, Fenner T, Lankisch PG. The role of antibiotic prophylaxis in the treatment of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology Clinics of North America 1999;28(3):641‐59. - PubMed
Rünzi 1999
-
- Rünzi M, Layer P. Nonsurgical management of acute pancreatitis. Use of antibiotics. Surgical Clinics of North America 1999;79(4):759‐65. - PubMed
Sandzén 2009
Sharma 2001
-
- Sharma VK, Howden CW. Prophylactic antibiotic administration reduces sepsis and mortality in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: a meta‐analysis. Pancreas 2001;22(1):28‐31. - PubMed
Steinberg 1994
-
- Steinberg W, Tenner S. Acute pancreatitis. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330(17):1198‐210. - PubMed
Tinto 2002
-
- Tinto A, Lloyd DAJ, Kang JY, Majeed A, Ellis C, Williamson RCN, Maxwell JD. Acute and chronic pancreatitis ‐diseases on the rise: a study of hospital admissions in England 1989/90 ‐ 1999/2000. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2002;16:2097‐105. - PubMed
Werner 2003
-
- Werner J, Uhl W, Hartwig W, Hackert T, Müller C, Strobel O, Büchler MW. Modern phase‐specific management of acute pancreatitis. Digestive Diseases 2003;21(1):38‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Werner 2005
Werner 2007
-
- Werner J, Hartwig W, Büchler MW. Antibiotic prophylaxis: An ongoing controversy in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2007;42:667‐72. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Villatoro 2003
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

