Single dose oral gabapentin for established acute postoperative pain in adults
- PMID: 20464764
- PMCID: PMC4170897
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008183.pub2
Single dose oral gabapentin for established acute postoperative pain in adults
Abstract
Background: Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug, also used in the treatment of neuropathic pain, which is the subject of a Cochrane review, currently under revision. Its efficacy in treating established acute postoperative pain has not been demonstrated.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy and safety of single dose oral gabapentin compared with placebo in established acute postoperative pain using methods that permit comparison with other analgesics.
Search strategy: We searched Cochrane CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Oxford Pain Relief Database. Additional studies were sought from reference lists of retrieved articles and reviews. Clinical trials databases were searched for unpublished studies; clinical trial reports of several unpublished studies have been made public following litigation in the US.
Selection criteria: Single oral dose, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of gabapentin for relief of established moderate to severe postoperative pain in adults.
Data collection and analysis: Studies were assessed for methodological quality and data extracted by two review authors independently. Numbers of participants with at least 50% of maximum possible total pain relief (TOTPAR) or summed pain intensity difference (SPID) with gabapentin or placebo were calculated and used to derive relative benefit (RB) or risk (RR), and number-needed-to-treat-to-benefit (NNT). Numbers of participants using rescue medication, and time to its use, were sought as additional measures of efficacy. Information on adverse events and withdrawals was collected.
Main results: Four unpublished studies met inclusion criteria; in three, participants had pain following dental surgery, and one followed major orthopaedic surgery; 177 participants were treated with a single dose of gabapentin 250 mg, 21 with gabapentin 500 mg, and 172 with placebo. At least 50% pain relief over 6 hours was achieved by 15% with gabapentin 250 mg and 5% with placebo; giving a RB of 2.5 (95% CI 1.2 to 5.0) and an NNT of 11 (6.4 to 35). Significantly fewer participants needed rescue medication within 6 hours with gabapentin 250 mg than with placebo; NNT to prevent use 5.8. About one third of participants reported adverse events with both gabapentin 250 mg and placebo. No serious adverse events occurred with gabapentin.
Authors' conclusions: Gabapentin 250 mg is statistically superior to placebo in the treatment of established acute postoperative pain, but the NNT of 11 for at least 50% pain relief over 6 hours with gabapentin 250 mg is of limited clinical value and inferior to commonly used analgesics. Gabapentin 250 mg is not clinically useful as a stand-alone analgesic in established acute postoperative pain, though this is probably the first demonstration of analgesic effect of an antiepileptic in established acute pain.
Conflict of interest statement
SD, SS, RAM & HJM have received research support from charities, government, academic, and industry sources at various times. This work was supported by NHS Cochrane Collaboration Grant and NIHR Biomedical Research Centre Programme. RAM and HJM have consulted for various pharmaceutical companies. RAM and HJM have received lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies related to analgesics and other healthcare interventions. PW is a full time employee of the UK Cochrane Centre.
Figures
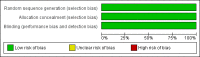






Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Additional references
Barden 2004
-
- Barden J, Edwards JE, McQuay HJ, Wiffen PJ. Relative efficacy of oral analgesics after third molar extraction. British Dental Journal 2004;197(7):407‐11. - PubMed
Clarke 2009
Collins 1997
-
- Collins SL, Moore RA, McQuay HJ. The visual analogue pain intensity scale: what is moderate pain in millimetres?. Pain 1997;72:95‐7. - PubMed
Collins 2001
-
- Collins SL, Edwards J, Moore RA, Smith LA, McQuay HJ. Seeking a simple measure of analgesia for mega‐trials: is a single global assessment good enough?. Pain 2001;91(1‐2):189‐94. - PubMed
Cook 1995
Cooper 1991
-
- Cooper SA. Single‐dose analgesic studies: the upside and downside of assay sensitivity. The design of analgesic clinical trials. Advances in Pain Research Therapy 1991;18:117‐24.
Derry 2009
Derry 2008
Derry 2009a
Derry 2009b
Jadad 1996a
-
- Jadad AR, Carroll D, Moore RA, McQuay H. Developing a database of published reports of randomised clinical trials in pain research. Pain 1996;66(2‐3):239‐46. - PubMed
Jadad 1996b
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Kissin 2009
Kong 2007
L'Abbe 1987
-
- L'Abbé KA, Detsky AS, O'Rourke K. Meta‐analysis in clinical research. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987;107:224‐33. - PubMed
Lloyd 2009
McQuay 2005
McQuay 2008
Moore 1996
Moore 1997a
Moore 1997b
Moore 1998
Moore 2003
-
- Moore RA, Edwards J, Barden J, McQuay HJ. Bandolier's Little Book of Pain. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2003. [ISBN: 0‐19‐263247‐7]
Moore 2005
Moore 2006
-
- Moore A, McQuay H. Bandolier's Little Book of Making Sense of the Medical Evidence. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006. [ISBN: 0‐19‐856604‐2]
Morris 1995
Striano 2008
Tiippana 2007
Toms 2008
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

