Interleukin (IL)-21-independent pathogen-specific CD8+ T-cell expansion, and IL-21-dependent suppression of CD4+ T-cell IL-17 production
- PMID: 20465570
- PMCID: PMC2967264
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03287.x
Interleukin (IL)-21-independent pathogen-specific CD8+ T-cell expansion, and IL-21-dependent suppression of CD4+ T-cell IL-17 production
Abstract
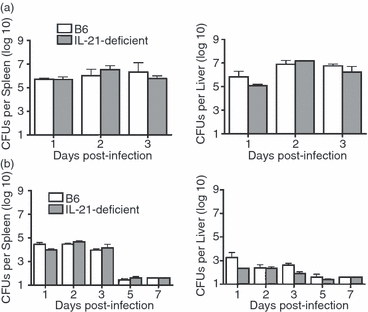
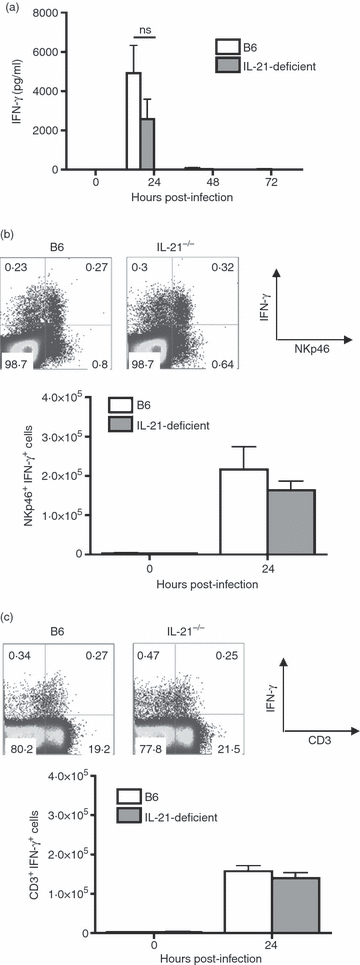
Although interleukin-21 (IL-21) potently activates and controls the differentiation of immune cells after stimulation in vitro, the role for this pleiotropic cytokine during in vivo infection remains poorly defined. Herein, the requirement for IL-21 in innate and adaptive host defence after Listeria monocytogenes infection was examined. In the innate phase, IL-21 deficiency did not cause significant defects in infection susceptibility, or in the early activation of natural killer and T cells. In the adaptive phase, L. monocytogenes-specific CD8(+) T cells expand to a similar magnitude in IL-21-deficient mice compared with control mice. Interestingly, the IL-21-independent expansion of L. monocytogenes-specific CD8(+) T cells was maintained even in the combined absence of IL-12 and type I interferon (IFN) receptor. Similarly, L. monocytogenes-specific CD4(+) T cells expanded and produced similar levels of IFN-γ regardless of IL-21 deficiency. Unexpectedly however, IL-21 deficiency caused significantly increased CD4(+) T-cell IL-17 production, and this effect became even more pronounced after L. monocytogenes infection in mice with combined defects in both IL-12 and type I IFN receptor that develop a T helper type 17-dominated CD4(+) T-cell response. Despite increased CD4(+) T-cell IL-17 production, L. monocytogenes-specific T cells re-expanded and conferred protection against secondary challenge with virulent L. monocytogenes regardless of IL-21 deficiency, or combined defects in IL-21, IL-12, and type I IFN receptor. Together, these results demonstrate non-essential individual and combined roles for IL-21, IL-12 and type I IFNs in priming pathogen-specific CD8(+) T cells, and reveal IL-21-dependent suppression of IL-17 production by CD4(+) T cells during in vivo infection.
© 2010 The Authors. Immunology © 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Innate IFN-γ is essential for programmed death ligand-1-mediated T cell stimulation following Listeria monocytogenes infection.J Immunol. 2012 Jul 15;189(2):876-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103227. Epub 2012 Jun 18. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22711893 Free PMC article.
-
Substantial in vivo proliferation of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocytes during secondary Listeria monocytogenes infection.Eur J Immunol. 2000 Apr;30(4):1053-9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(200004)30:4<1053::AID-IMMU1053>3.0.CO;2-N. Eur J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10760793
-
Deviation from a strong Th1-dominated to a modest Th17-dominated CD4 T cell response in the absence of IL-12p40 and type I IFNs sustains protective CD8 T cells.J Immunol. 2008 Mar 15;180(6):4109-15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.6.4109. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18322221 Free PMC article.
-
Confounding roles for type I interferons during bacterial and viral pathogenesis.Int Immunol. 2013 Dec;25(12):663-9. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxt050. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Int Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24158954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of interleukin-21 in HIV infection.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012 Aug-Oct;23(4-5):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012. PMID: 22763176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of IL-17 promotes spinal cord neuroinflammation via activation of the transcription factor STAT3 after spinal cord injury in the rat.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:786947. doi: 10.1155/2014/786947. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 24914249 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-21 Induces Short-Lived Effector CD8+ T Cells but Does Not Inhibit Their Exhaustion after Mycobacterium bovis BCG Infection in Mice.Infect Immun. 2018 Jul 23;86(8):e00147-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00147-18. Print 2018 Aug. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29844233 Free PMC article.
-
Innate IFN-γ is essential for programmed death ligand-1-mediated T cell stimulation following Listeria monocytogenes infection.J Immunol. 2012 Jul 15;189(2):876-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103227. Epub 2012 Jun 18. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22711893 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal Listeria monocytogenes susceptibility despite preconceptual priming and maintenance of pathogen-specific CD8(+) T cells during pregnancy.Cell Mol Immunol. 2014 Nov;11(6):595-605. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.84. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Cell Mol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25242275 Free PMC article.
-
B7-1/B7-2 blockade overrides the activation of protective CD8 T cells stimulated in the absence of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2013 Aug;94(2):367-76. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0313118. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23744647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brandt K, Singh PB, Bulfone-Paus S, Ruckert R. Interleukin-21: a new modulator of immunity, infection, and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007;18:223–32. - PubMed
-
- Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A, et al. Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature. 2000;408:57–63. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki K, Spolski R, Feng CG, et al. A critical role for IL-21 in regulating immunoglobulin production. Science (New York, NY) 2002;298:1630–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

