Anti-TNF-alpha therapy does not ameliorate disease in a model of acute virus-endotoxin mediated respiratory disease in pigs
- PMID: 20466438
- PMCID: PMC2922464
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.04.003
Anti-TNF-alpha therapy does not ameliorate disease in a model of acute virus-endotoxin mediated respiratory disease in pigs
Abstract
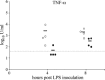
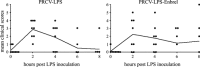
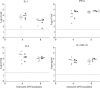
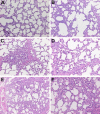
Tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) has been shown to play a role in many inflammatory conditions. Currently anti-TNF-alpha drugs (e.g. etanercept) are used in humans for treatment of autoimmune diseases. In this study we aimed to elucidate the role of TNF-alpha in the development of virus-endotoxin-induced respiratory disease. Twenty-two caesarean derived colostrum deprived pigs were used. Initially, the availability in the lungs and circulation, and possible clinical and inflammatory effects of etanercept alone were assessed in 4 pigs after intratracheal and intraperitoneal administration of 0.5mg/per route/per pig. High anti-TNF-alpha activity was detected in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluids, peritoneal lavage fluids and serum of all animals for at least 8h post-inoculation (HPI). No clinical symptoms, lung lesions, lung cell infiltration or induction of IFN-alpha, IL-1, IL-6, IL-12 and TNF-alpha in BAL were detected. Subsequently, the ability of etanercept to block porcine TNF-alpha and its effect on the above mentioned parameters and on lung virus titres were assessed in 8 pigs. They were inoculated intratracheally with porcine respiratory coronavirus (PRCV) followed by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) 24h later. Etanercept was administered at the time of LPS inoculation via the same routes and dose as in the initial experiment. The parameters were compared with a control group (n=8), receiving only PRCV-LPS. Half of the animals from each group were euthanized at 4 and the rest at 8h after LPS inoculation. TNF-alpha was completely neutralized in 3 of the 4 animals euthanized at 4 HPI and significantly lower than in the PRCV-LPS group at all times. No significant differences in disease severity, lung lesions, virus replication, lung cell infiltration or levels of IFN-alpha, IL-1, IL-6 and IL-12/IL-23 were observed between the two groups. Blocking of TNF-alpha alone was not sufficient to ameliorate disease in the PRCV-LPS model of respiratory disease, possibly due to the redundancy in the proinflammatory cytokine cascade, or the involvement of other unidentified disease mediators.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A potential role for tumour necrosis factor-alpha in synergy between porcine respiratory coronavirus and bacterial lipopolysaccharide in the induction of respiratory disease in pigs.J Med Microbiol. 2000 Jul;49(7):613-620. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-7-613. J Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10882086
-
Interaction between porcine reproductive-respiratory syndrome virus and bacterial endotoxin in the lungs of pigs: potentiation of cytokine production and respiratory disease.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Mar;41(3):960-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.3.960-966.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12624016 Free PMC article.
-
Differential production of proinflammatory cytokines in the pig lung during different respiratory virus infections: correlations with pathogenicity.Res Vet Sci. 1999 Aug;67(1):47-52. doi: 10.1053/rvsc.1998.0277. Res Vet Sci. 1999. PMID: 10425240 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo studies on cytokine involvement during acute viral respiratory disease of swine: troublesome but rewarding.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002 Sep 10;87(3-4):161-8. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(02)00047-8. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002. PMID: 12072230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The combination of PRRS virus and bacterial endotoxin as a model for multifactorial respiratory disease in pigs.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2004 Dec 8;102(3):165-78. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2004.09.006. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2004. PMID: 15507303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Active implications for dermatologists in 'SARS-CoV-2 ERA': Personal experience and review of literature.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Aug;34(8):1626-1632. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16646. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020. PMID: 32426855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Pathogenesis of Bovine and Porcine Respiratory Coronaviruses in the Animal Host Species and SARS-CoV-2 in Humans.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Jul 23;58(8):e01355-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01355-20. Print 2020 Jul 23. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32522830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations between immune-suppressive and stimulating drugs and novel COVID-19-a systematic review of current evidence.Ecancermedicalscience. 2020 Mar 27;14:1022. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2020.1022. eCollection 2020. Ecancermedicalscience. 2020. PMID: 32256705 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bastos K.R., Marinho C.R., Barboza R., Russo M., Alvarez J.M., D’Imperio Lima M.R. What kind of message does IL-12/IL-23 bring to macrophages and dendritic cells? Microbes Infect. 2004;6:630–636. - PubMed
-
- Helle M., Boeije L., Aarden L.A. Functional discrimination between interleukin 6 and interleukin 1. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988;18:1535–1540. - PubMed
-
- Jackson J.M. TNF-alpha inhibitors. Dermatol. Ther. 2007;20:251–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

