Rab GEFs and GAPs
- PMID: 20466531
- PMCID: PMC2929657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.04.007
Rab GEFs and GAPs
Abstract
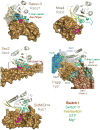
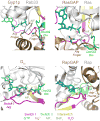
Rabs are GTP-binding proteins with conserved functions in membrane trafficking. They are regulated by a diverse group of structurally unrelated GDP-GTP exchange factors (GEFs), and a family of GTP-hydrolysis activating proteins (GAPs) containing the conserved TBC domain. Recent structural and cell biological studies shed new light on the mechanisms of Rab GEF and GAP action, and the cellular trafficking pathways they act in.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Pereira-Leal JB, Hume AN, Seabra MC. Prenylation of Rab GTPases: molecular mechanisms and involvement in genetic disease. FEBS Lett. 2001;498:197–200. - PubMed
-
- Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC. The mammalian Rab family of small GTPases: definition of family and subfamily sequence motifs suggests a mechanism for functional specificity in the Ras superfamily. J Mol Biol. 2000;301:1077–1087. - PubMed
-
- Gillingham AK, Munro S. Long coiled-coil proteins and membrane traffic. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1641:71–85. - PubMed
-
- Zerial M, McBride H. Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:107–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

