Linking molecular motors to membrane cargo
- PMID: 20466533
- PMCID: PMC3393125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.04.008
Linking molecular motors to membrane cargo
Abstract
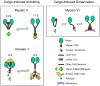
Three types of motors, myosins, kinesins, and cytoplasmic dynein, cooperate to transport intracellular membrane organelles. Transport of each cargo is determined by recruitment of specific sets of motors and their regulation. Targeting of motors to membranes often depends on the formation of large multiprotein assemblies and can be influenced by membrane lipid composition. Motor activity can be regulated by cargo-induced conformational changes such as unfolding or dimerization. The architecture and function of motor: cargo complexes can also be controlled by phosphorylation, calcium signaling, and proteolysis. The complexity of transport systems is further increased by mechanical and functional cross-talk between different types of motors on the same cargo and by participation of the same motor in the movement of different organelles.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Kamal A, Stokin GB, Yang Z, Xia CH, Goldstein LS. Axonal transport of amyloid precursor protein is mediated by direct binding to the kinesin light chain subunit of kinesin-I. Neuron. 2000;28:449–459. - PubMed
-
- Vallee RB, Williams JC, Varma D, Barnhart LE. Dynein: An ancient motor protein involved in multiple modes of transport. J Neurobiol. 2004;58:189–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

