Klotho: a novel phosphaturic substance acting as an autocrine enzyme in the renal proximal tubule
- PMID: 20466874
- PMCID: PMC2923354
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.10-154765
Klotho: a novel phosphaturic substance acting as an autocrine enzyme in the renal proximal tubule
Abstract
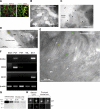
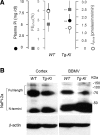
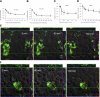
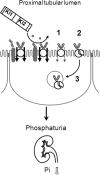
Klotho has profound effects on phosphate metabolism, but the mechanisms of how Klotho affects phosphate homeostasis is unknown. We detected Klotho in the proximal tubule cell, brush border, and urinary lumen, where phosphate homeostasis resides. Increasing Klotho in the kidney and urine chronically by transgenic overexpression or acutely by intravenous infusion caused hypophosphatemia, phosphaturia from decreased proximal phosphate reabsorption, and decreased activity and protein of the principal renal phosphate transporter NaPi-2a. The phosphaturic effect was present in FGF23-null mice, indicating a direct action distinct from Klotho's known role as a coreceptor for FGF23. Direct inhibition of NaPi-2a by Klotho was confirmed in cultured cells and in cell-free membrane vesicles characterized by acute inhibition of transport activity followed by decreased cell surface protein. Transport inhibition can be mimicked by recombinant beta-glucuronidase and is associated with proteolytic degradation and reduced surface NaPi-2a. The inhibitory effect of Klotho on NaPi-2a was blocked by beta-glucuronidase inhibitor but not by protease inhibitor. Klotho is a novel phosphaturic substance that acts as an enzyme in the proximal tubule urinary lumen by modifying glycans, which cause decreased transporter activity, followed by proteolytic degradation and possibly internalization of NaPi-2a from the apical membrane.
Figures


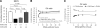
References
-
- Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Kawaguchi H, Suga T, Utsugi T, Ohyama Y, Kurabayashi M, Kaname T, Kume E, Iwasaki H, Iida A, Shiraki-Iida T, Nishikawa S, Nagai R, Nabeshima Y I. Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature. 1997;390:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Shiraki-Iida T, Iida A, Nabeshima Y, Anazawa H, Nishikawa S, Noda M, Kuro-o M, Nabeshima Y. Improvement of multiple pathophysiological phenotypes of klotho (kl/kl) mice by adenovirus-mediated expression of the klotho gene. J Gene Med. 2000;2:233–242. - PubMed
-
- Segawa H, Yamanaka S, Ohno Y, Onitsuka A, Shiozawa K, Aranami F, Furutani J, Tomoe Y, Ito M, Kuwahata M, Tatsumi S, Imura A, Nabeshima Y, Miyamoto K-i. Correlation between hyperphosphatemia and type II Na/Pi cotransporter activity in klotho mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292:F769–F779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK041612/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK067158/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019712/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK048482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R29 DK048482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-20543/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK-079328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK020543/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG025326/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK41612/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-48482/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG25326/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG19712/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079328/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067158/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

