Toward an integrated structural model of the 26S proteasome
- PMID: 20467039
- PMCID: PMC2938054
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.R000002-MCP201
Toward an integrated structural model of the 26S proteasome
Abstract
The 26S proteasome is the end point of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and degrades ubiquitylated substrates. It is composed of the 20S core particle (CP), where degradation occurs, and the 19S regulatory particle (RP), which ensures substrate specificity of degradation. Whereas the CP is resolved to atomic resolution, the architecture of the RP is largely unknown. We provide a comprehensive analysis of the current structural knowledge on the RP, including structures of the RP subunits, physical protein-protein interactions, and cryoelectron microscopy data. These data allowed us to compute an atomic model for the CP-AAA-ATPase subcomplex. In addition to this atomic model, further subunits can be mapped approximately, which lets us hypothesize on the substrate path during its degradation.
Figures


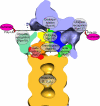
References
-
- Murata S., Yashiroda H., Tanaka K. (2009) Molecular mechanisms of proteasome assembly. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 104–115 - PubMed
-
- Glickman M. H., Ciechanover A. (2002) The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol. Rev. 82, 373–428 - PubMed
-
- Voges D., Zwickl P., Baumeister W. (1999) The 26S proteasome: a molecular machine designed for controlled proteolysis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 1015–1068 - PubMed
-
- Jentsch S., Haendler B. (2009) The Ubiquitin System in Health and Disease, Springer, Heidelberg, Germany - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

