Long-term increase in CD4+ T-cell counts during combination antiretroviral therapy for HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 20467286
- PMCID: PMC3018341
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32833adbcf
Long-term increase in CD4+ T-cell counts during combination antiretroviral therapy for HIV-1 infection
Abstract
Objective: To inform guidelines concerning when to initiate combination antiretroviral therapy (ART), we investigated whether CD4(+) T-cell counts (CD4 cell counts) continue to increase over long periods of time on ART. Losses-to-follow-up and some patients discontinuing ART at higher CD4 cell counts hamper such evaluation, but novel statistical methods can help address these issues. We estimated the long-term CD4 cell count trajectory accounting for losses-to-follow-up and treatment discontinuations.
Design: The study population included 898 US patients first initiating ART in a randomized trial (AIDS Clinical Trials Group 384); 575 were subsequently prospectively followed in an observational study (AIDS Clinical Trials Group Longitudinal Linked Randomized Trials).
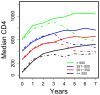
Methods: Inverse probability of censoring weighting statistical methods were used to estimate the CD4 cell count trajectory accounting for losses-to-follow-up and ART discontinuations, overall and for pretreatment CD4 cell count categories (<or=200, 201-350, 351-500, and >500 cells/microl).
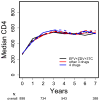
Results: Median CD4 cell count increased from 270 cells/microl pre-ART to an estimated 556 cells/microl at 3 and 532 cells/microl at 7 years after starting ART in analyses ignoring treatment discontinuations, and to 570 and 640 cells/microl, respectively, had all patients continued ART. However, even had ART been continued, an estimated 25, 9, 3, and 2% of patients with pretreatment CD4 cell counts of 200 or less, 201-350, 351-500, and more than 500 cells/microl would have had CD4 cell counts of 350 cells/microl or less after 7 years.
Conclusion: If patients remain on ART, CD4 cell counts increase in most patients for at least 7 years. However, the substantial percentage of patients starting therapy at low CD4 cell counts who still had low CD4 cell counts after 7 years provides support for ART initiation at higher CD4 cell counts.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00000919 NCT00001137.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest: Dr. Hughes is a paid member of Data and Safety Monitoring Boards for Boehringer-Ingelheim, Medicines Development Ltd, Pfizer and Tibotec. These companies are all manufacturers or developers of antiretroviral therapy or other therapy for HIV infection. In the past year and currently, Dr. Benson has served on advisory boards for GlaxoSmithKline and Merck, and served on a Data and Safety Monitoring Board for Achillion, Dr. Collier receives research support from Merck & Co. and Schering-Plough, has served on advisory boards for GlaxoSmithKline and Pfizer, is a member of a Data and Safety Monitoring Board for Merck & Co., and owns stock in Abbott Laboratories and Bristol Myers Squibb. In the past year, Dr. Robbins was a consultant for Johnson and Johnson.
Figures

References
-
- Hammer SM, Eron JJ, Reiss P, Schooley RT, Thompson MA, Walmsley S, et al. Antiretroviral treatment of adult HIV infection: 2008 recommendations of the International AIDS Society-USA panel. JAMA. 2008;300:555–570. - PubMed
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Washington, DC: Department of Health and Human Services; Nov 32008. [Accessed 12/09/2009]. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents; pp. 1–139. (Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/AdultandAdolescentGL001226.pdf.)
-
- Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Department of Health and Human Services; Dec 12009. [Accessed 12/09/2009]. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in HIV-1-infected adults and adolescents; pp. 1–161. (Available at http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/contentfiles/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf.)
-
- Wilkin TJ, Gulick RM. When to start antiretroviral therapy? Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:1580–1586. - PubMed
-
- Phillips AN, Emery S. Predicting the potential benefits of early initiation of ART: time to do a trial to find out. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2009;4:165–166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- AI 38855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69428/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI46376/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR024156/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AL69415/PHS HHS/United States
- AI 38858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69467/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI38858-09S1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI25859-19/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-69465/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI32782/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 062435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27658/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI25879/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI46370/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69447/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69501/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27675/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01-AI069484/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI054907/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM048704/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI062435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069511-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69477/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069434/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27664/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR00051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UO1-AI 032783-14/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30AI050410(-11)/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27661/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM48704/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI069439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR00044/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI 069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI34853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000046-48/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI69418/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024643/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI024643/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069452/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UOI-A1069556/PHS HHS/United States
- AI46381/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00533/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR000750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI27665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069470/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354 A0104/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5-P30-AI-045008-09/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 68634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27673/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR00047/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI-069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069450/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR00096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR-00052/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 68636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI 51164/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051164/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5-MO1 RR00044/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI 024643/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UO1 AI069495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI50409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69532/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

