The SYK tyrosine kinase: a crucial player in diverse biological functions
- PMID: 20467426
- PMCID: PMC4782221
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2765
The SYK tyrosine kinase: a crucial player in diverse biological functions
Abstract
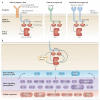
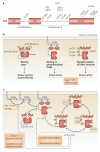
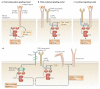
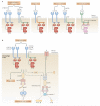
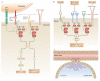
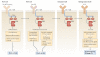
Spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) is known to have a crucial role in adaptive immune receptor signalling. However, recent reports indicate that SYK also mediates other, unexpectedly diverse biological functions, including cellular adhesion, innate immune recognition, osteoclast maturation, platelet activation and vascular development. SYK is activated by C-type lectins and integrins, and activates new targets, including the CARD9-BCL-10-MALT1 pathway and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Studies using Drosophila melanogaster suggest that there is an evolutionarily ancient origin of SYK-mediated signalling. Moreover, SYK has a crucial role in autoimmune diseases and haematological malignancies. This Review summarizes our current understanding of the diverse functions of SYK and how this is being translated for therapeutic purposes.
Figures
Comment on
-
Natural killer T cells: Limiting B cell autoimmunity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 Jun;10(6):384. doi: 10.1038/nri2796. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20514674 No abstract available.
References
-
- Reth M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature. 1989;338:383–4. - PubMed
-
- Mócsai A, et al. The immunomodulatory adapter proteins DAP12 and Fc receptor γ-chain (FcRγ) regulate development of functional osteoclasts through the Syk tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:6158–63. - PMC - PubMed
-
Together with refs ,, this paper demonstrated that SYK activation through DAP12 and FcRγ is required for osteoclast development and bone resorption
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

