Isolation of nebulin from rabbit skeletal muscle and its interaction with actin
- PMID: 20467585
- PMCID: PMC2868979
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/108495
Isolation of nebulin from rabbit skeletal muscle and its interaction with actin
Abstract
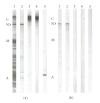
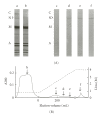
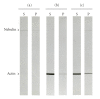
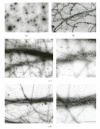
Nebulin is about 800 kDa filamentous protein that binds the entire thin filament of vertebrate skeletal muscle sarcomeres. Nebulin cannot be isolated from muscle except in a completely denatured form by direct solubilization of myofibrils with SDS because nebulin is hardly soluble under salt conditions. In the present study, nebulin was solubilized by a salt solution containing 1 M urea and purified by DEAE-Toyopearl column chromatography via 4 M urea elution. Rotary-shadowed images of nebulin showed entangled knit-like particles, about 20 nm in diameter. The purified nebulin bound to actin filaments to form loose bundles. Nebulin was confirmed to bind actin, alpha-actinin, beta-actinin, and tropomodulin, but not troponin or tropomyosin. The data shows that full-length nebulin can be also obtained in a functional and presumably native form, verified by data from experiments using recombinant subfragments.
Figures



References
-
- Labeit S, Kolmerer B. The complete primary structure of human nebulin and its correlation to muscle structure. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1995;248(2):308–315. - PubMed
-
- Labeit S, Gibson T, Lakey A, et al. Evidence that nebulin is a protein-ruler in muscle thin filaments. FEBS Letters. 1991;282(2):313–316. - PubMed
-
- Wang K. Purification of titin and nebulin. Methods in Enzymology B. 1982;85:264–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

